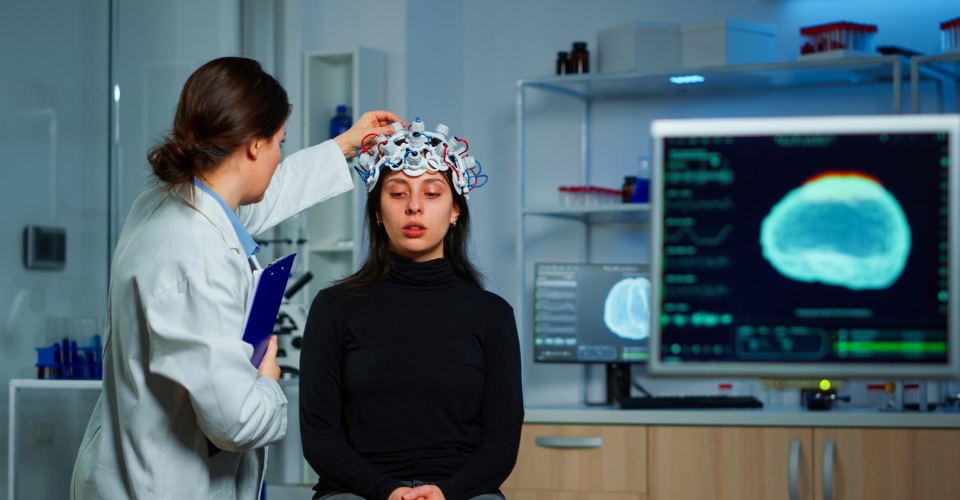
In a groundbreaking research finding from the University of Southern Denmark, a new door has been opened to the therapeutic potential of psilocybin, the active compound found in psychedelic mushrooms, through microdosing.
This discovery marks a significant step forward in the quest to harness the healing properties of this ancient substance for the treatment of mental disorders.
Psilocybin has long been revered as a classic psychedelic substance, known for inducing profound altered states of consciousness and mystical experiences.
Recent years have seen a surge of interest in the potential therapeutic applications of psilocybin, particularly in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as depression and addiction.
Traditionally, therapeutic psilocybin treatment involves administering a high dose of the compound to a patient after thorough therapeutic preparation. This is followed by a guided psychedelic experience in the presence of a trained therapist.
The subsequent integration of this experience takes place over several therapy sessions, helping patients process and derive lasting benefits from their journey.
Current Experiments and Hospital-Based Trials For Considering the Potential of Psilocybin
To explore the therapeutic potential of psilocybin, experiments are currently underway in hospitals, including Bispebjerg Hospital and Rigshospitalet. These trials aim to evaluate the efficacy of psilocybin-assisted therapy as a treatment option for various psychiatric disorders, particularly depression and addiction.
One key aspect of these experiments is the utilization of microdosing—a method that involves administering small, sub-perceptual doses of psilocybin.
Unlike full-dose psychedelic experiences, microdosing does not induce the intense hallucinatory effects typically associated with psilocybin. Instead, it allows patients to experience subtle changes in perception, mood, and cognition without overwhelming their senses.
The concept of microdosing is gaining traction as a promising avenue for therapeutic intervention. By employing small doses of psilocybin, patients may benefit from its potential mood-enhancing and cognitive-enhancing effects without the need for intense psychedelic experiences.
This approach could provide a gentler, more accessible means of harnessing psilocybin’s therapeutic potential.
Integral to the success of psilocybin-assisted therapy is the process of integration. Patients work with therapists to make sense of their experiences, gain insights, and develop coping strategies. This integration process helps individuals incorporate the lessons learned during their psilocybin journeys into their everyday lives, facilitating lasting positive change.
The ongoing experiments with psilocybin and microdosing offer a glimmer of hope for individuals grappling with mental disorders that have proven resistant to conventional treatments.
Depression, addiction, and related conditions have taken a significant toll on individuals and societies worldwide. Exploring alternative therapies like psilocybin-assisted treatment reflects a commitment to finding innovative solutions to these pressing challenges.
While the research into psilocybin’s therapeutic potential is promising, it is not without its challenges and ethical considerations. Ensuring the safety and well-being of patients, as well as adhering to legal and regulatory frameworks, remains paramount.
Furthermore, the stigma surrounding psychedelics and the need for further rigorous scientific investigation present hurdles to mainstream acceptance and adoption. However, as the evidence accumulates and the positive outcomes of these therapies become increasingly evident, there is hope for a shift in the perception of these ancient substances.
The research from the University of Southern Denmark signifies a pivotal moment in the journey to unlock the therapeutic potential of psilocybin. As experiments with microdosing and psilocybin-assisted therapy continue, the hope is that these groundbreaking treatments may offer a lifeline to those struggling with mental disorders.
By combining ancient wisdom with modern science, the therapeutic landscape is evolving, offering new possibilities for healing and recovery in the realm of mental health.