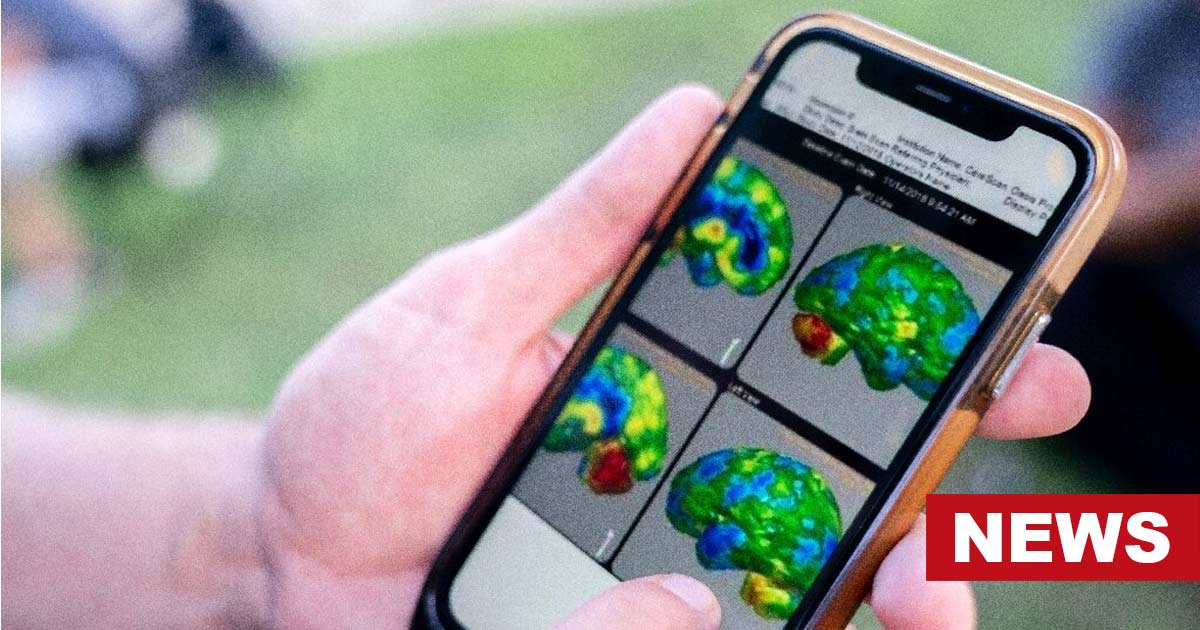
In a significant development last summer, Psychology Today reported on a comprehensive analysis that dealt a decisive blow to the long-standing myth of the chemical imbalance depression theory. This outdated notion, which suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of serotonin, has been repeatedly debunked over the past few decades.
However, it continues to persist in the public consciousness, possibly due to the influence of pharmaceutical industry propaganda and media oversimplification. Interestingly, some prominent psychiatrists led a serotonin-debunking study, claiming that the serotonin theory of depression is being promoted as part of an anti-psychiatry conspiracy to boost pharmaceutical sales.
Researchers who have a vested financial interest in the serotonin theory of depression have come together to challenge and attempt to debunk the findings of the study. However, a closer examination reveals that their concerns are largely technical, contradictory, and in some cases, outright false, according to the authors of the serotonin-debunking study.
None of the critics provide solid or consistent evidence supporting serotonin’s role in depression. Rather, their minor objections seem to highlight the efforts of pharmaceutical industry-funded researchers clinging to a poorly supported, controversial, and outdated theory, which nonetheless serves to bolster the marketing of new drugs. The authors of the challenging study, led by Joanna Moncrieff, responded to the criticism and engaged in a debate that was published in Molecular Psychiatry.
Among the critics of the serotonin-debunking study is Jacob Jacobsen, the founder and CEO of Evecxia Therapeutics, a company focused on marketing a serotonin-targeting drug. Another group of authors led by Sameer Jauhar also voiced their objections. Notably, this group has a significant number of financial conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry.
These critics argue that serotonin should still be considered the primary cause of depression, despite their inability to provide valid or consistent evidence to support this claim. Additional critics, such as Abbas F. Almulla and Michael Maes, argue that serotonin itself is not directly linked to depression but propose that a serotonin precursor is the actual cause.
A critic and researcher Lucie Bartov suggests that depression involves a complex and poorly understood system encompassing various parts of the brain, including the serotonin system. Researcher Rif S. El-Mallakh also acknowledges that the serotonin theory of depression has long been debunked, but they contend that Moncrieff’s group is mistaken in highlighting how this undermines the evidence base for antidepressant drugs.
The authors of the serotonin-debunking study argue against the efficacy of SSRIs for depression, noting their minimal advantage over placebos and the potential for placebo effects or unrelated factors.
They express concerns about marketing drugs based on unproven neurotransmitter hypotheses and emphasize the public’s perception of medications correcting imbalances versus those with poorly understood effects. They criticize vague and un-testable hypotheses and emphasize the need for valid, scientifically testable theories.
They caution against assuming a drug treats a condition solely because it alleviates symptoms, using the analogy of self-medicating with alcohol. They highlight the complexity and debate surrounding serotonin’s role in depression. Joanna Moncrieff took to Twitter to answer the critics’ inquiries around the serotonin-debunking study.
The research team challenged criticisms regarding their review, defending their inclusion and exclusion criteria and the assessment methods used. They asserted that their criteria were clearly stated and aligned with validated guidelines, such as AMSTAR, STREGA, and GRADE measures.
They refuted Jauhar’s claims as false and argue that their review was comprehensive and unbiased. They dismissed the critics’ accusations of cherry-picking, emphasizing that the additional studies cited do not provide convincing evidence for a link between low serotonin and depression. They also accused their critics of attempting to discredit their research to perpetuate the myth of an established biological basis for depression.