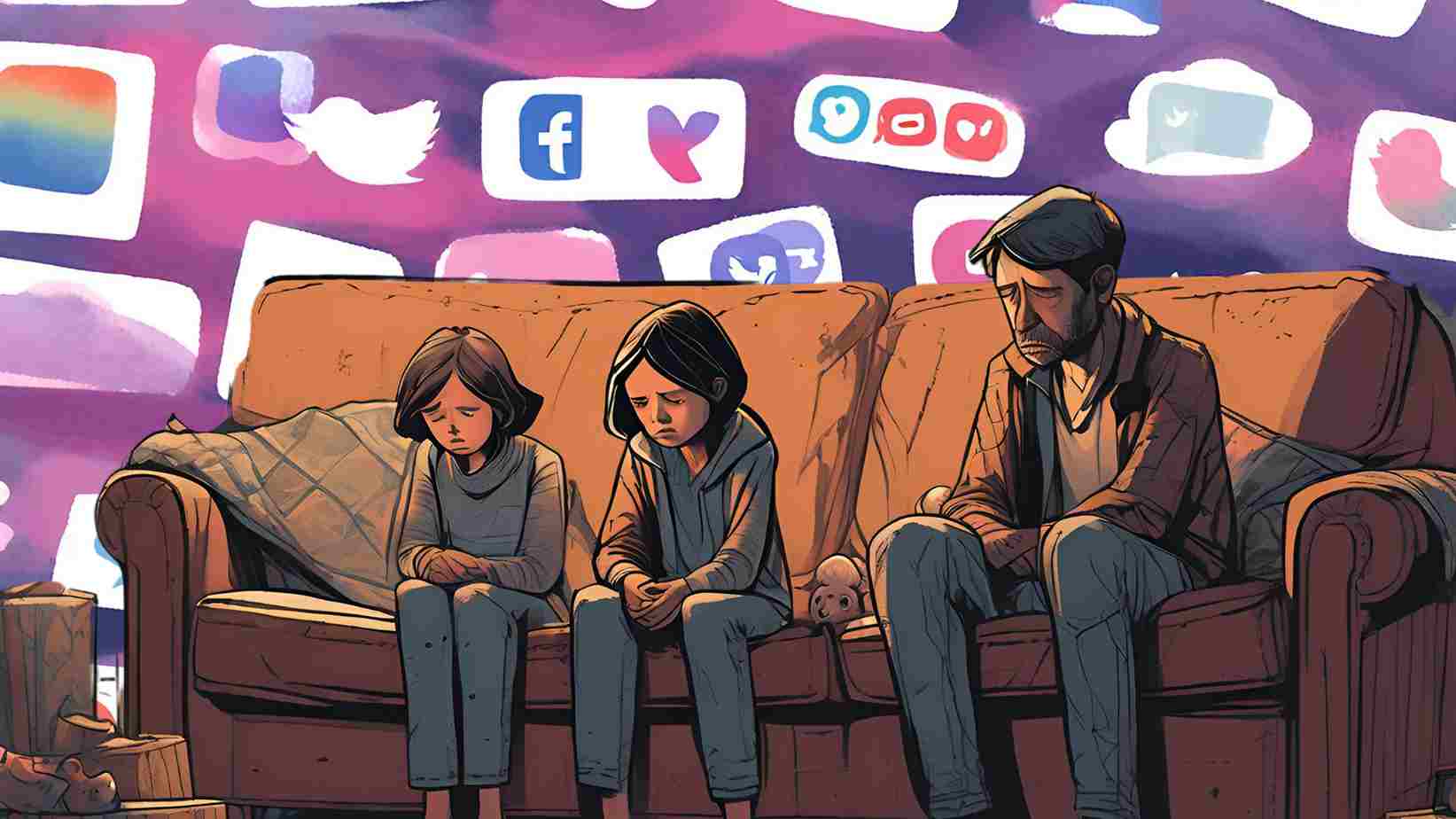
A recent study led by UCL researchers has shed light on how consuming negative online content affects mental health, particularly for parents. The study, published in Nature Human Behaviour, suggests that excessive exposure to negative content can lead to parental depression, worsened mood, and poor mental health. Experts warn about the growing impact of social media on mental well-being and offer practical advice for families.
Key Findings:
- Negative Web-Browsing and Mental Health:
According to the study, individuals who engaged in “self-guided web-browsing” filled with negative content reported worse mental health outcomes. The study found that people who were already in a bad mood often turned to more negative content, creating a cycle of depression and anxiety. - The Emotional Contagion Theory:
Ms. Ashi Tomar, a senior psychologist, explains that this phenomenon aligns with the emotional contagion theory. This theory suggests that individuals “mirror” the emotions of what they consume. Therefore, consuming negative content leads to negative feelings like sadness, anxiety, and even anger. - Confirmation Bias and Cognitive Overload:
The study also highlighted confirmation bias, where individuals unconsciously seek more negative content to match their mood. This reinforces negative thinking, increasing stress and burnout, especially in parents facing already challenging situations. - Impact on Different Age Groups:
- Adolescents (10-19 years): Teens who are exposed to negative content online can develop issues like social anxiety, self-image concerns, and poor academic performance.
- Young Adults and Middle-Aged Individuals (20-59 years): This group may experience burnout, job stress, sleep disturbances, and depression due to negative online content.
- Older Adults: The elderly may face loneliness, paranoia, or vulnerability to scams due to the influence of negative online material.
Parental Depression Linked to Negative Online Content
The study from UCL researchers highlights the deeper issues caused by negative online content, especially for parents already dealing with challenges like epilepsy challenges. The research shows a clear connection between the type of content consumed and worsening mental health, including parental depression.
Psychological Impact of Negative Content:
When individuals repeatedly engage with negative online material, it can distort their outlook on life. According to Ms. Ashi Tomar, a senior psychologist, this pattern contributes to heightened emotional distress. She explains that repeated exposure to negative online content fuels stress and depressive thoughts, leading to feelings of helplessness. For parents of children with epilepsy, who already face overwhelming daily challenges, this can further deepen feelings of anxiety and despair.
The study reports that the more negative content a person consumes, the more their mood and mental health deteriorate. This is especially troubling for parents, who are often responsible for managing their children’s health and well-being. Epilepsy challenges, such as frequent seizures and developmental delays in children, already place considerable stress on parents. Adding the burden of negative content on social media can intensify feelings of burnout, depression, and anxiety.
7 Ways to Combat Negative Scrolling:
Ms. Tomar offers helpful strategies to deal with the harmful effects of negative online content:
- Limit Social Media Use: Set a time limit for daily usage and stick to it.
- Avoid Social Media Close to Bedtime: Refrain from scrolling during meals, right after waking up, or before going to sleep.
- Engage in Alternate Hobbies: Replace negative online time with productive and enjoyable activities.
- Practice Digital Detox: Take regular breaks from screens to relax and unwind.
- Follow Positive Content: Follow accounts that promote positivity, motivation, and inspiration.
- Spend Time with Loved Ones: Physical interactions with family and friends can lift your mood.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult a mental health professional if feelings of anxiety or depression persist.
The Need for Further Research:
Experts agree that more studies are needed to understand how online content influences individuals, especially parents. Early interventions and support systems are necessary to help mitigate the epilepsy challenges and emotional strain many face.
With the rise of digital platforms, it is crucial for parents to recognize the impact of their online habits and make conscious choices for better mental health and overall well-being.























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.