Psychology News – Researchers have recently developed a way to determine when acting on one’s worst impulses verges on pathological. The study found that when a person’s emotions run high, it can be correlated with how fast the person reacts to stimulating visuals, especially disturbing ones.
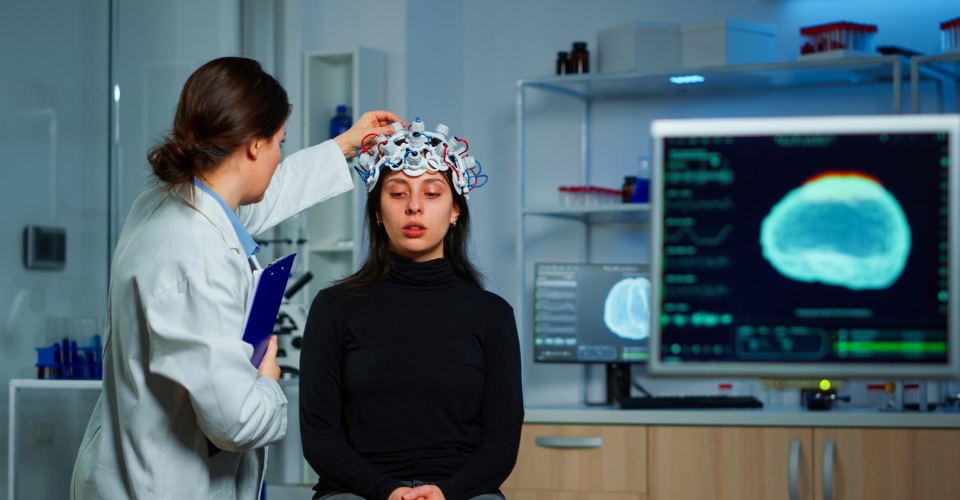
In a new study, researchers at the University of California have developed an “emotional stop-signal task” to evaluate negative urgency which is a clinical form of impulsivity linked to eating disorders, depression, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, self-harm, and ADHD.
They assigned 450 adults including 150 psychiatric patients and filled out the UPPS-P Impulsive Behavior Scale to rate the participants on positive and negative urgency. Then the participants viewed a fast-moving series of photos on a computer screen and categorized each image as either positive or negative.
The study findings showed that when faced with unpleasant images, participants who scored highly on the negative urgency scale experienced more difficulty while keeping their finger off the button, even when a stop button appeared.
However, the results remained consistent after 61 psychiatric patients took the behavioral test twice, once while hospitalized and again, up to six months later, after being released. After testing the task’s reliability over a longer period of time, the result indicated the stability of the test protocol. The research result showed that participants whose self-assessment signaled poor impulse control were extremely fast on the trigger and they frequently reacted to the photo even before the stop sign appeared.
“The results suggest that some people have more trouble controlling impulses that are driven by negative emotions. This is significant because, in a worst-case scenario, negative emotion-related impulsivity can lead to extreme behaviors like self-harm and suicide,” said J.D. Allen, co-author of the study.
To Know More You May Refer To:
Allen, K. J., Johnson, S. L., Burke, T. A., Sammon, M. M., Wu, C., Kramer, M. A., Wu, J., Schatten, H. T., Armey, M. F., & Hooley, J. M. (2021). Validation of an emotional stop-signal task to probe individual differences in emotional response inhibition: Relationships with positive and negative urgency. Brain and Neuroscience Advances, 5, 239821282110582. https://doi.org/10.1177/23982128211058269


























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.