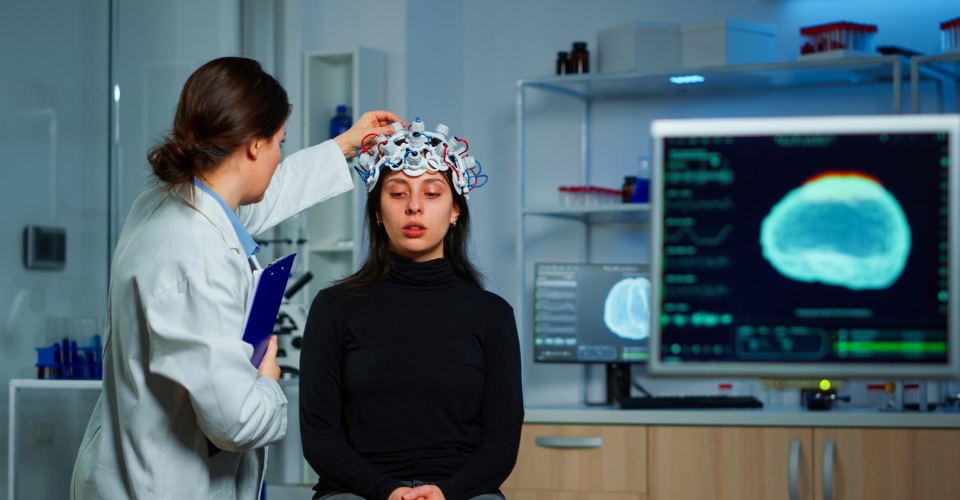
Brain News: The sense of smell activates different brain areas. Researchers from Ruhr-University Bochum found that the structures of the olfactory sense work closely together with the brain’s reward and aversion systems. It means scents are processed not only by the olfactory center but also by regions responsible for emotions and valence determination.
So far there are very few studies on olfactory perception and researchers do not clearly know how olfactory memories are formed. The new study focused on clarifying to what extent brain structures that aren’t part of the olfactory system are involved in olfactory memory formation.
The researchers combined electrophysiological stimulation with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and obtained a detailed picture of the neuronal structures that responded to the stimulation of the olfactory bulb. With the help of fluorescence in situ hybridisation analysis of neuronal gene expression, the team analysed highly responsive structures. This technique helps researchers determine whether neurons do indeed store the olfactory stimulus: This event serves as evidence of memory formation. Stimulation of the olfactory bulb had led to altered gene activity, even in the nerve cells of the limbic cortex — associated with the processing of emotions.
“The involvement of these non-olfactory structures probably plays a key role in the storage of olfactory experiences,” says Dr. Christina Strauch, interpreting the findings. “We deduce from this that rodents quickly categorise perceived scents as pleasant or unpleasant while smelling them.”
The study results indicate that the olfactory system works closely with the brain’s reward and aversion systems in both learning and memory formation. The findings provide an additional theoretical basis for understanding why the sense of smell plays such a unique role in the formation and retrieval of memories.
To Know More You May Refer To:
Strauch, C., Hoang, T., Angenstein, F., & Manahan-Vaughan, D. (2021). Olfactory information storage engages subcortical and cortical brain regions that support valence determination. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhab226


























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.