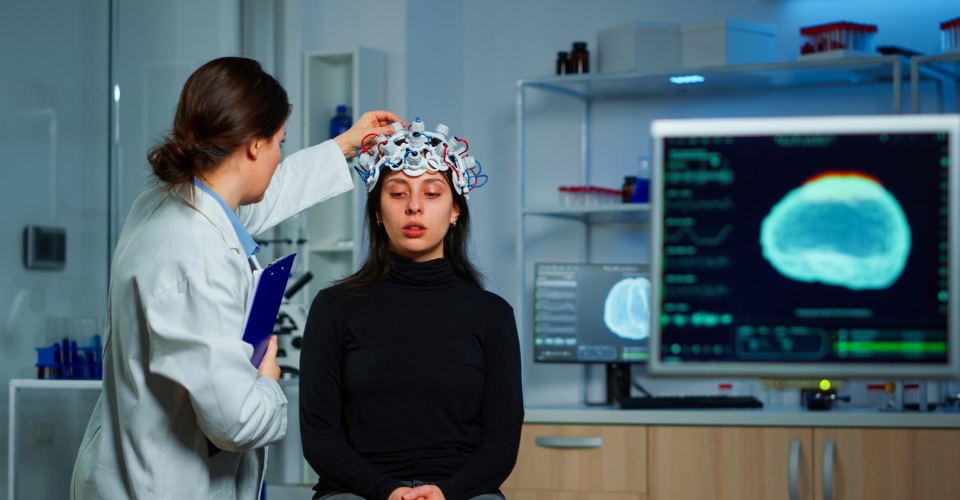
Brain News: Japanese scientists have identified 33 metabolic compounds within the blood linked to dementia. It could be key to new methods of diagnosis and treatment of dementia.
Dementia is one of the most serious aging-related diseases, characterised by a slow but typically irreversible decline in the ability to remember, think, decide, solve problems or perform day-to-day activities. An estimated 55 million people are living with dementia globally. Scientists still do not know the exact cause of dementia and methods as to how it can be detected and treated.
Metabolites are chemical substances produced by vital chemical reactions that occur within cells and tissues. The levels of the metabolites in our body are in balance, but fluctuate as we age or develop dementia.
In the new study published in PNAS, the research team collected and analysed blood samples from 8 dementia patients, 8 healthy elderly patients and 8 healthy young people to use as a reference. The team measured the levels of 124 different metabolites in whole blood and found that 33 metabolites, split into 5 different sub-groups, correlated with dementia. 7 of the compounds increased in dementia patients, while 26 of them showed decreased in level. 20, including nine that were abundant in red blood cells, of these compounds had not previously been linked to dementia.
The results revealed that the levels of 33 metabolites differed in patients with dementia, compared to elderly people with no existing health conditions. This indicates that red blood cells do not just deliver oxygen but also crucial metabolites that protect the nervous system from damage. Identification of the 33 metabolites is a sign scientists are one step closer to being able to molecularly diagnose dementia.
To Know More You May Refer To:
Teruya, T., Chen, Y., Kondoh, H., Fukuji, Y., & Yanagida, M. (2021). Whole blood metabolomics of dementia patients reveal classes of disease-linked metabolites. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.22.449525


























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.