In a remarkable collaboration involving 34 researchers from 18 institutions, a groundbreaking study has shed light on the efficacy and safety of psilocybin, the psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, as a potential treatment for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial, conducted at 11 research sites across the United States from December 2019 to June 2022, marks a significant step forward in our understanding of novel approaches to addressing this debilitating mental health condition.
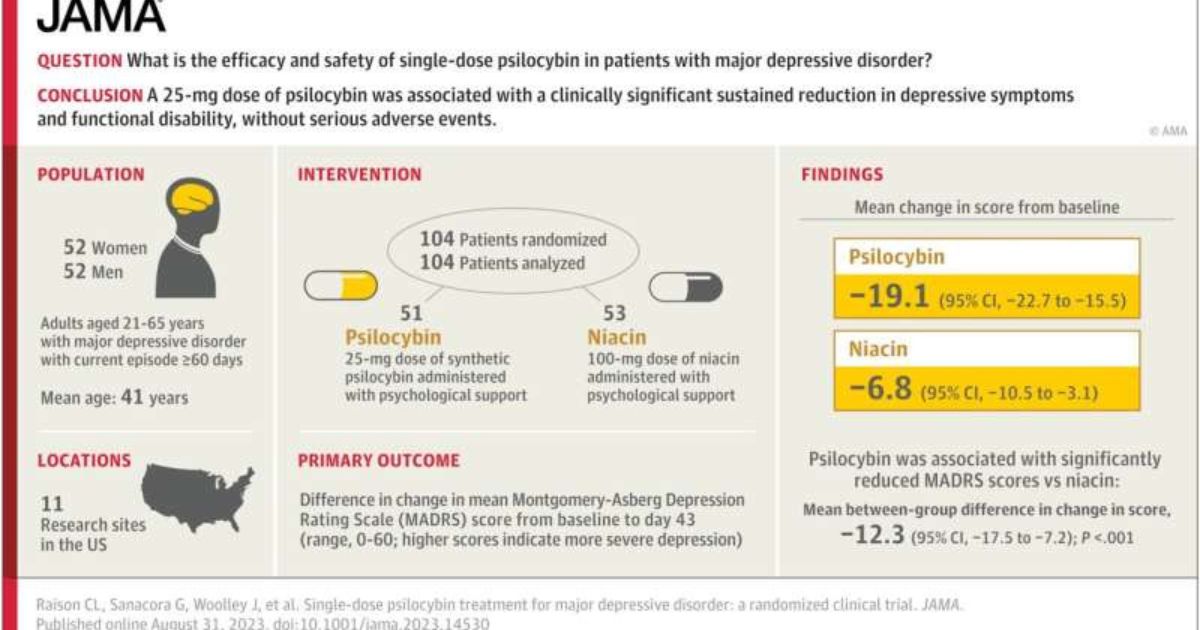
The study enrolled 104 adults diagnosed with MDD, each experiencing moderate or severe symptoms.
Long-Lasting Effects Of Psilocybin On Major Depressive Disorder
Participants in this pioneering study were administered either a single 25mg dose of psilocybin or a 100mg dose of niacin, a placebo control, in conjunction with psychological support.
This carefully designed trial sought to explore both the short-term and long-term effects of psilocybin on individuals grappling with MDD.
To gauge the impact of psilocybin treatment, researchers employed a range of assessment tools.
The primary measurement was the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), a 10-item questionnaire that assesses core mood symptoms of depression, including sadness, tension, lassitude, pessimistic thinking, and suicidal thoughts.
Notably, psilocybin treatment resulted in a significant reduction in MADRS scores compared to the niacin control group, both on day eight and day 43 after dosing.
Furthermore, the Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS), which evaluates work, social, and family life disability, also exhibited substantial improvements in the psilocybin-treated group compared to the placebo group from baseline to day 43.
The study delved into several exploratory outcomes to gain a comprehensive understanding of psilocybin’s impact on MDD.
These included assessments using the Clinical Global Impressions Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire, Symptoms of Major Depressive Disorder Scale, and the Oxford Depression Questionnaire, designed to evaluate emotional blunting.
Remarkably, the findings showcased the broader positive effects of psilocybin treatment beyond symptom reduction. Participants undergoing psilocybin therapy reported improvements in global disease severity, self-reported depressive and anxiety symptoms, and enhanced overall quality of life.
What sets psilocybin apart is its apparent ability to achieve these improvements without the common side effect of emotional blunting frequently associated with conventional antidepressant medications.
This groundbreaking study offers a glimmer of hope for those grappling with Major Depressive Disorder.
Psilocybin, when administered in a controlled and supervised setting, appears to hold the potential to not only alleviate depressive symptoms but also enhance overall mental well-being.
The results indicate that this treatment positively impacts various facets of mental health, including reducing anxiety symptoms, improving overall functioning, and boosting quality of life.
The implications of these findings are profound. For decades, the treatment landscape for depression has primarily revolved around conventional antidepressant medications, often with limited success and side effects that can hinder patients’ daily lives.
Psilocybin, as a novel and seemingly effective alternative, could potentially revolutionize the field of mental health treatment.
However, it is essential to recognize that this study is just the beginning. Further research and clinical trials are necessary to validate these promising findings and determine the optimal dosage, treatment protocols, and long-term effects of psilocybin therapy.
Additionally, rigorous safety measures and professional guidance are imperative when considering the use of this substance for therapeutic purposes.
In conclusion, this collaborative effort has illuminated a potential breakthrough in the treatment of Major Depressive Disorder.
Psilocybin, administered under controlled conditions, has shown the capacity to not only alleviate symptoms but also improve the overall well-being of individuals living with depression.
While further research is needed, these findings offer a glimmer of hope for those seeking effective alternatives to traditional antidepressant medications.