In recent years, the landscape of everyday conversations has been significantly shaped by the lexicon of therapy and mental health.
Phrases like “coping mechanisms,” “traumas,” and “attachment styles” have become commonplace, alongside more clinical terms such as “OCD,” “anxiety disorders,” and “bipolarity.” The terminology of therapy, including words like “gaslighting,” “catharsis,” and “narcissistic behavior,” has infiltrated popular discourse to such an extent that it’s often referred to as “Instagram therapy.”
However, the consequences of using these terms out of context are worth examining, as they may inadvertently trivialize the very essence of therapy.
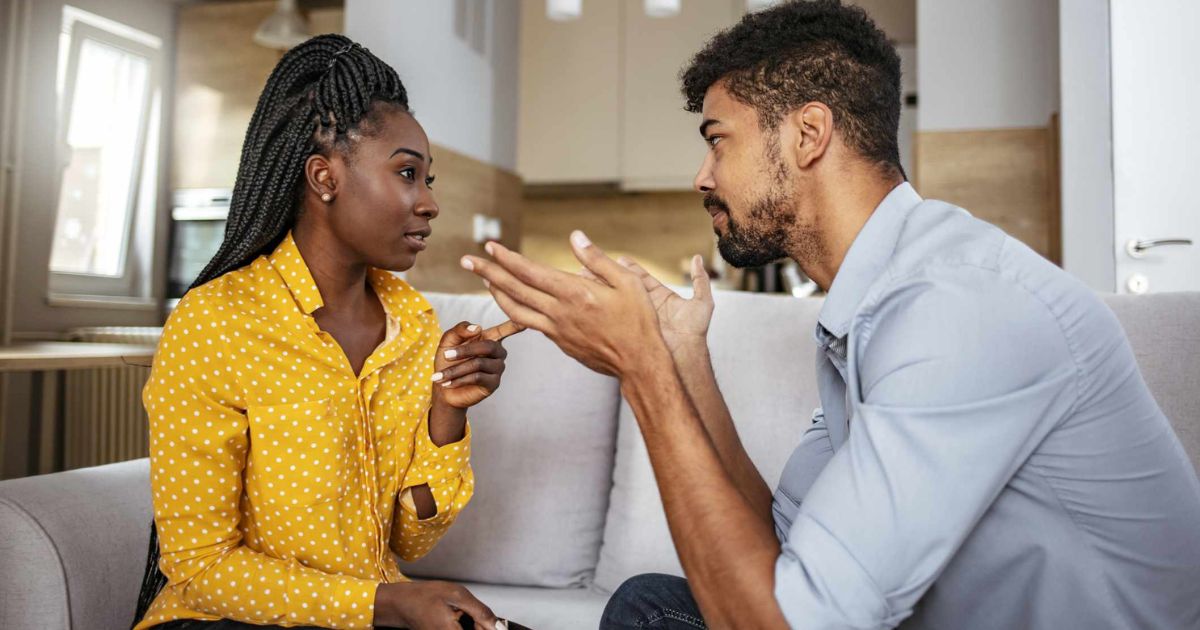
The phenomenon known as “therapy speak” involves the incorrect yet authoritative use of psychotherapeutic jargon and mental health terminology. In today’s digital age, where social media platforms like Instagram play a significant role in shaping public conversations, the misuse of these terms has become increasingly prevalent.
Understand The Influence of Therapy Speak
For instance, a casual post on Instagram by a user named Melvin Thomas highlighted how discussions about personal issues often invoke terms associated with therapy. Thomas shared, “When discussing my professional issues with a friend, he suggested focusing on the future.
I was deeply hurt because I didn’t feel heard.” In this scenario, the user received unquestioning validation from followers without considering the context. This raises the question: does the “idiot compassion” of social media overshadow the “wise compassion” provided by trained professionals?
Furthermore, experts have raised concerns about the misappropriation of certain terms, such as “triggers.” In clinical settings, patients are encouraged to confront discomfort and triggers through controlled exposure to facilitate their therapeutic progress.
In contrast, within therapy-speak, the term “trigger” often implies the need to avoid or eliminate anything that causes discomfort. This misinterpretation of terminology can lead to a lack of understanding regarding the role of triggers in mental health treatment.
The implications of therapy-speak extend beyond casual conversations. They have the potential to influence our perception of mental health, leading to the trivialization of therapy itself. Using mental health terms loosely can result in the exaggeration of symptoms and the neglect of underlying issues.
Meera Ravi, a psychologist and author of “Counseling: What, Why, and How,” underscores the risks of self-diagnosing. According to Ravi, the careless use of mental health terms may exacerbate feelings of anxiety and depression, ultimately increasing the risk of self-harm and other dangerous behaviors. Consequently, there is a pressing need for caution when employing therapy-related vocabulary in non-clinical contexts.
Consider the case of Vinita*, an analyst at a Mumbai bank, who once described her relationship with her sibling as “abusive,” frequently using terms like “gaslighting” and “toxic behavior.” Vinita’s perspective on her relationship shifted after she encountered a book titled “Maybe You Should Talk to Someone” by Lori Gottlieb, ironically on Instagram.
This prompted her to seek professional therapy, and in the process, she realized that the conflicts with her sibling were not manifestations of gaslighting, but rather differences in opinions. Reflecting on this experience, she remarked, “We used such damning labels for each other.”
The prevalence of therapy-speak in everyday conversations has inadvertently transformed many individuals into armchair therapists, equipped with an extensive mental health vocabulary. While this increased awareness is positive in some respects, there is also a downside.
Meera Ravi, the psychologist, emphasizes the importance of exercising caution when using such terms. When clients assert, “I have OCD” or “I have depression,” it is essential to explore deeper to ascertain whether these labels accurately reflect their experiences. The careless and imprecise use of these terms can lead to an inaccurate understanding of one’s mental health, potentially compounding existing issues.
In summary, the proliferation of therapy-speak in everyday conversations is a double-edged sword. While it has led to increased awareness and dialogue surrounding mental health, the misuse and misappropriation of therapy-related terms can have detrimental consequences.
It is essential to approach these terms with caution, to avoid the exaggeration of symptoms and the neglect of underlying issues. By doing so, we can ensure that discussions about mental health remain productive and supportive rather than inadvertently harmful.