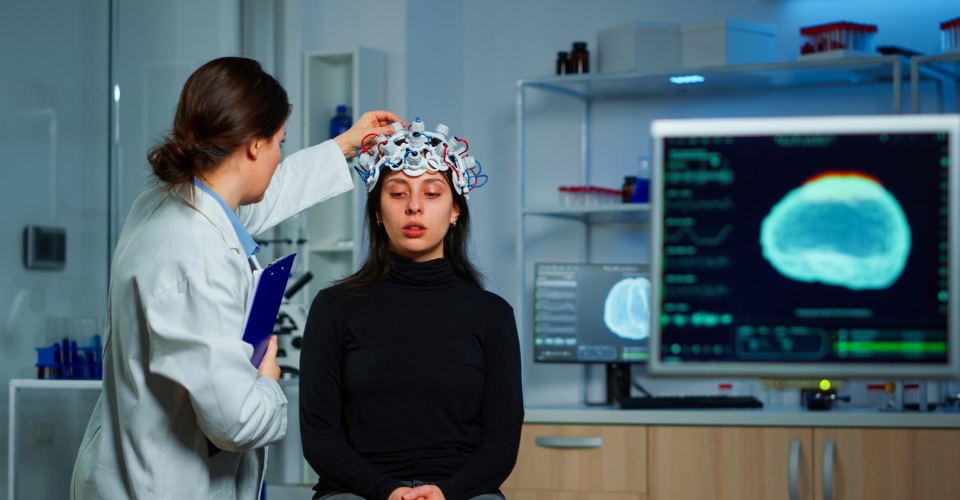
Brain News – A new theory finds links between forgetting, engram cell-accessibility in the brain, and environmental dictates. It also highlights the difference between “natural forgetting” due to altered memory access and pathological memory loss. The study also ventures into diseases associated with pathological forgetting, exploring the role of hijacked natural forgetting mechanisms in specific contexts.
A study, published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience, reveals that changes in the human ability to access specific memories are based on environmental feedback and predictability.
The newly formulated theory hypothesizes that memories are stored in “engram cells” (ensembles of neurons) and that successful recollection involves reactivation of these cells. In supplemental logic, forgetting occurs when these engram cells fail to get reactivated. In fact, all the different forms of forgetting occur when circuit modeling—conditioned by environmental feedback and predictability—-switches engram cells from an accessible state (where they can be reactivated by natural recall cues) to an inaccessible state (where they cannot be reactivated). Such variations of forgetting are also dictated by time course, reversibility, and other underlying mechanisms. With this, the established hypothesis seeks to label forgetting as a form of neuroplasticity that alters engram cell-accessibility according to environmental dictates so as to enable dynamic interaction with the environment.
Though the end consequence is lost information, the study claims that this “natural forgetting” due to altered memory access is different from memory loss. It even states the benefits of this functional feature of the brain that results in positive wellbeing, such as the inducement of behavioral flexibility, better decision-making skills, and enabling more relevant and relatable interaction with the current environment.
The new theory proposed by Dr Tomás Ryan (Associate Professor in the School of Biochemistry and Immunology and the Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience at Trinity College Dublin) and Dr Paul Frankland (Professor in the Department of Psychology at the University of Toronto and the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto) ventures furthermore into diseases associated with pathological forgetting or memory loss.
Both state in this context, “Importantly, we believe that this ‘natural forgetting’ is reversible in certain circumstances, and that in disease states — such as in people living with Alzheimer’s disease for example — these natural forgetting mechanisms are hijacked, which results in greatly reduced engram cell accessibility and pathological memory loss.”
To Know More You May Relate To
Ryan, T. J., & Frankland, P. W. (2022). Forgetting as a form of adaptive engram cell plasticity. Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 10.1038/s41583-021-00548-3. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-021-00548-3


























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.