In a groundbreaking move, a dedicated group of researchers at China University of Geosciences have found compelling evidence supporting moderate, regular exercise as an effective antidote for tackling post-partum depression among women.
Their exhaustive study that was published by the open-access journal PLOS ONE has combined 26 past research to rip through and expose the far-reaching implications of exercising among women with post-partum depression.
What is Postpartum Depression?
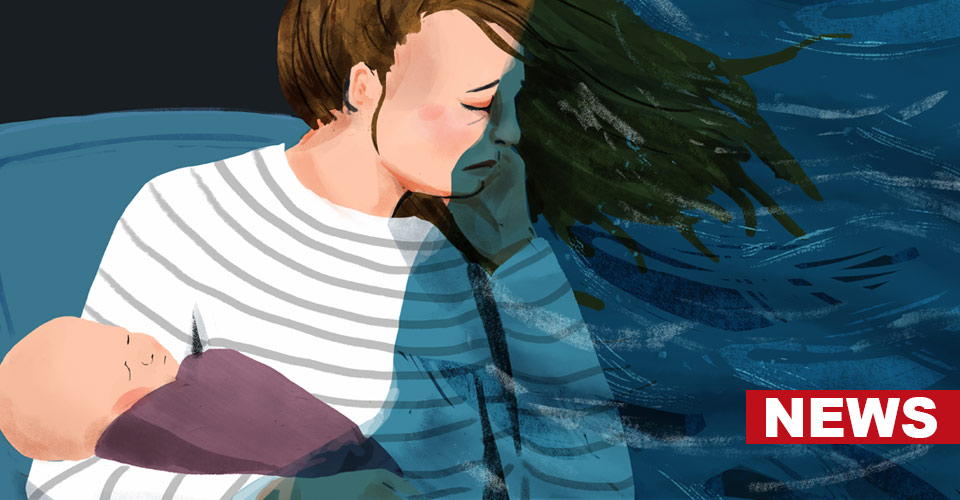
Post partum depression is a severe mood disorder that follows child-birth in women. Several studies have noted that majority—between 50% and 75%—of women display some form of depressive symptoms after delivery.
Shockingly, around 10% and 15% are affected with severe issues leading to diagnosis as postpartum depression.
This condition is not merely about depressive symptoms alone; it encompasses anxiety, sleep disorders and extreme mood swings making it multifaceted.
Alternative Therapies for Post-Partum Depression: A Quest
Over the years, medical scientists have tried to come up with remedies to reduce these distressing symptoms.
Nonetheless, most conventional treatments have undesirable side effects necessitating the need to find alternative treatments that do not involve use of drugs.
One of various approaches explored is exercise as a potential method used in relieving symptoms linked to postnatal depression.
Probing Exercise’s Role
Considering how exercise might be an option for therapy, this ground-breaking study aimed at revealing other aspects related to its effectiveness was carried out by them.
Earlier findings suggested positive impacts from exercise but lacked comprehensive investigations which were necessary for defining specific types and dosages of exercises.
The researchers therefore closely examined twenty-six research concerning postpartum depressions’ effect on aerobic exercises as well as their types and hours or time spent.
Revelations from the Research
The outcomes relayed by the research team exposed an interesting correlation whereby aerobic workouts could bring about significant changes particularly assisting women who go through postpartum depression.
Additionally, this study found that activities such as jogging, walking or swimming were quite beneficial.
By raising heart rate and respiration, these exercises improved blood circulation thereby increasing levels of neurotransmitters in the brains.
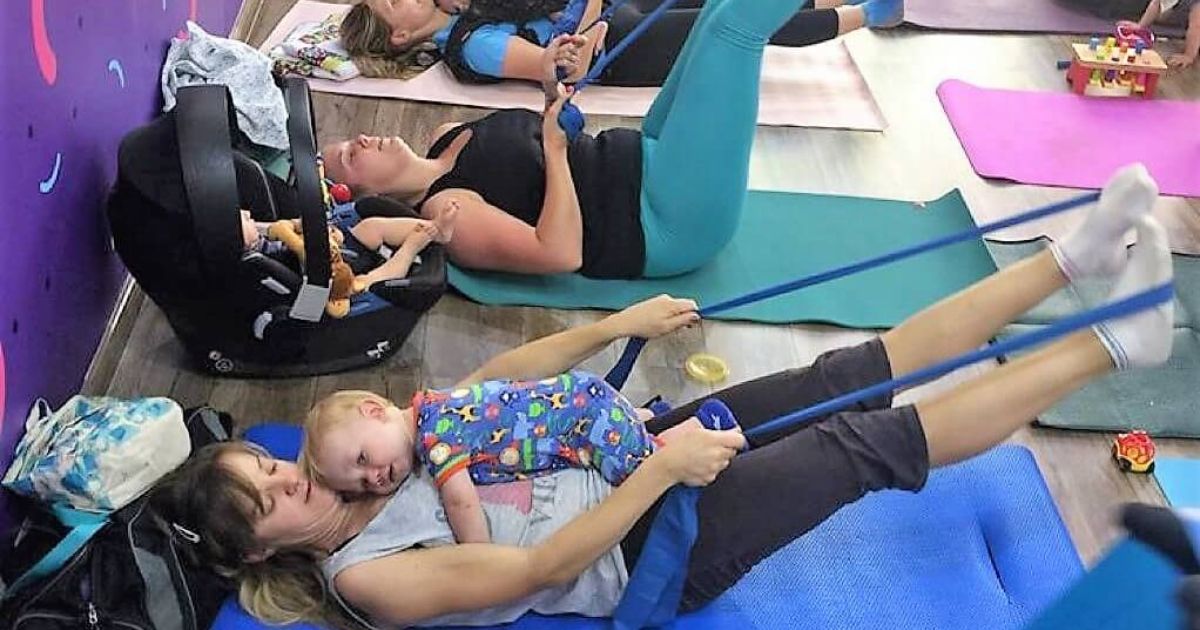
Group Dynamics and Exercise: A Potent Combination
Additionally, the researchers discovered a very interesting fact-positive results were more pronounced when exercise was done within group settings than when individual sessions were done while exercising.
It seemed as if the communal nature of team-based exercising magnified its therapeutic effects by possibly creating supportive environments that can help relieve post-partum symptoms.
Optimal Duration of Exercise
Besides just discoursing on the exercise types’ effectiveness and social dynamics, the research was more into defining the ideal type of exercise program.
The researchers realized that carrying out moderate exercise for 35 to 45 minutes three or four times weekly is considered one of the best prescriptions in mitigating symptoms associated with postpartum blues.
Future Implications
Implications of these findings are far reaching, and they provide a ray of hope to mothers with postpartum depression.
Additionally, the validation of exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention, through detailed insights on the most suitable types, social settings, and durations, opens door for more specific and effective treatment strategies.
Furthermore, it is an essential focal point for postpartum care that must include exercise integration aimed at reducing the effects of this common mood disorder.
In conclusion, fundamentally, this brilliant effort by China University of Geosciences not only supports the healing aspect of exercise but also sets forth important conditions which help to gauge its effectiveness in combating postpartum depression.
This path breaking study unravels a deeper understanding about how engaging in physical activities related to certain types of sport or just any other activity can be an effective means to alleviate distressing symptoms characteristic for postnatal depression.
They have underpinned new course in non-pharmacological interventions for women who are in such difficult circumstances.