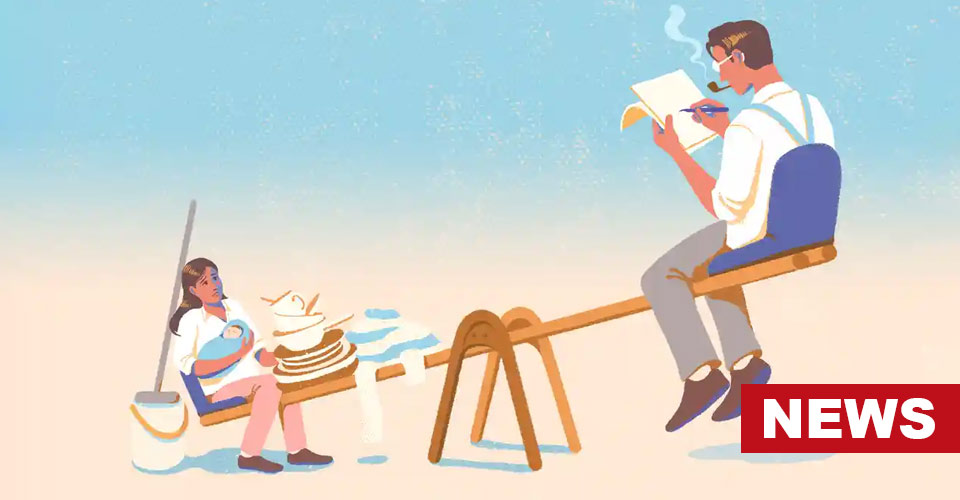
- Recent studies answered the heatedly debated question “Do men do less housework?”.
- Experts point to the link between gender roles and inequality in household labor.
Emerging research, testifying to existing research, confirmed that gendered inequality also extends to the domestic division of labor. A recent group of researchers explained why women still do more household chores than men with the help of the “affordance theory”.
Understanding The “affordance Theory”
James J. Gibson, the founder of ecological psychology, in 1979, formulated a radical evidence-based approach to describe the relationships between organisms and their environments. Called the “affordance theory”, it promoted a better understanding of the human perceptual system and how visual perception is linked to action.
Why Do Men Do Less Housework?
A recent study tapped into the affordance theory to explain the inequitable distribution of domestic and caring labor in different-sex couples.
The researchers point to the gender disparity in the perception of affordances for domestic tasks. Men’s perception of domestic tasks differs from women’s, due to gendered orientations and differentiated societal perceptions.
In comparison to women, men do not harbor the perception of affordances for domestic tasks such as emptying the dishwasher, sweeping the floor, or tidying a mess. Unlike the former, the latter tends to treat domestic work as a hobby or a free choice.
This inequality in household labor often goes unnoticed by male partners and contributes to gender inequality on a larger scale.
These findings are in line with previous research that confirmed that gender ideology seems to determine the percentage of household tasks willingly taken up by men and women in shared households. It also generates a differential meaning about household chores for men and women.
Gender Inequality In Household Labor: Examples
Recent studies reveal that:
- Women spend more time than men in traditionally female household chores.
- Women perceive their male partners to be much less involved in everyday household chores and only focused on occasional household chores traditionally considered masculine.
- There is a 22% difference between working men and women when it comes to doing household chores. Women who work at least 35 hours a week spend 4.9 hours on household work, while men who work those same hours spend 3.8 hours on household work.
- Married mothers who earn more than their husbands take on an even greater share of the housework and caregiving responsibilities, in comparison to the fathers.
Mental Health Impact Of Unequal Labor Division
Unpaid domestic and cognitive labor has negative mental health consequences for women. Gender inequality in the domestic division of labor is associated with greater scores of negative interactions and partner conflicts. Overworked women shouldering the greater share of household tasks tend to develop:
- Depressive symptoms
- Irritability and frustration
- Anger issues
- Work stress
- Negative attitudes, bordering on rejection, criticism, and maltreatment
- Mental health conditions like anxiety disorders, mood disorders, substance use disorders, etc.
Addressing The Inequality In Household Labor
Research roots the reason why men don’t do as many household tasks to gender roles. To address it, most public and welfare policies have suggested the monetization of domestic work.
However, the most effective measure includes breaking gender stereotypes and equally dividing the household work.
For parents, engaging children in gender-related educational discussions and equally assigning them household tasks can go a long way in promoting gender equality.
Know More About –
Related Articles –
- 10 Safety Tips For Domestic Violence
- How Domestic Abusers Groom And Isolate Their Victims
- 10 Things You Should Never Tolerate In A Relationship