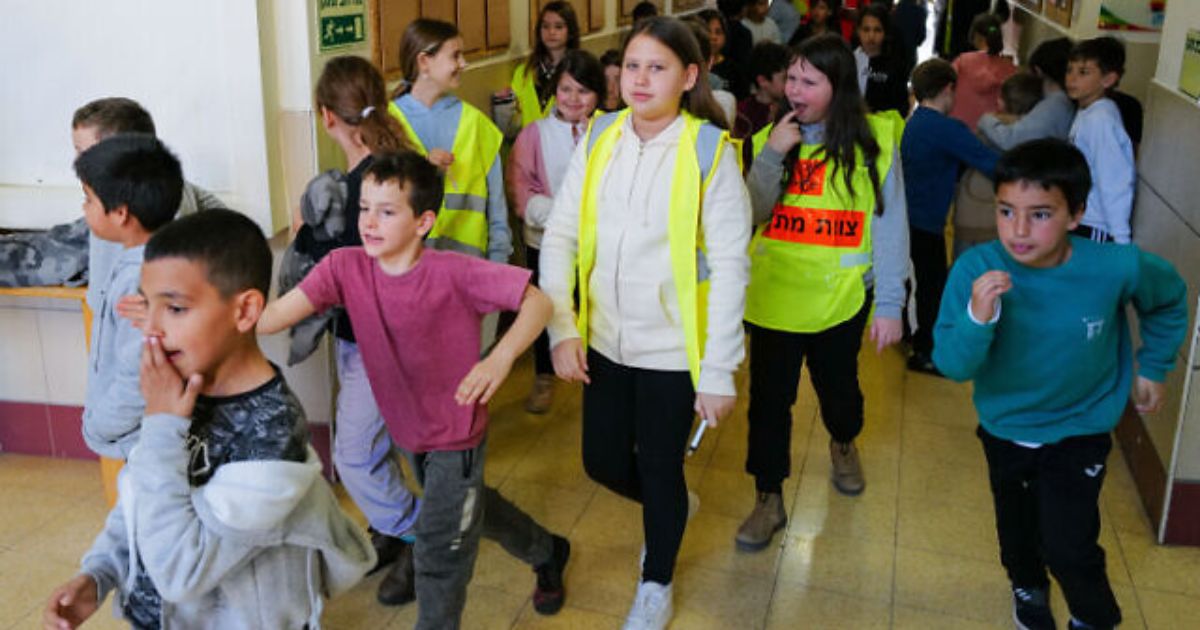
Some concerns have emerged about the resultant psychological problems on children, even including impacts on those not directly affected but have been influenced by the consequences of October 7 tragedies and the ongoing southern conflict.
Chava Friedman, the director of psychology at the Ministry of Education, spoke with The Times of Israel in a very insightful conversation.
There he offered an in-depth analysis of the complex and multilayered dynamics that are currently affecting how children and their caregivers navigate and understand their behavior amid the difficulties and heartbreaks of this time.
During their developmental phase, children demonstrate an extraordinary acuity in perception.
In the perception of unfolding events, there is a combination of different stimuli that include subtle facial expressions by parents or caretakers, overhearing conversations and watching television programs which contain visual images.
As a result, this sensory input contributes immensely to their growing knowledge about the environment.
Dr. Friedman added that children only make sense of reality based on their family homes and communities.
Dr. Friedman mentioned that typical age-appropriate behaviors that are out-of-place may be indicative of stress when asked about signs of behavioral distress.
For instance, a preschooler who insists on sleeping with his parent during heightened tension might show anxiety signs.
Bedwetting, increased sensitivity to sounds having siren-like qualities alternating sleep patterns and inability for younger kids to concentrate may also be seen in other cases.
With increasing age these can change into aggression or avoidance of responsibilities or even risk-taking behavior in young adults.
Preserving a sense of stability during turmoil was highlighted by Dr. Friedman as being crucial for children’s well-being.
These consistencies could include regular visits to friends despite fear in order to provide comfort and normalcy.
This becomes significant when giving guidance based on specific scenarios; connection was emphasized by Dr. Friedman particularly from someone important in a child’s life.
In order to pacify anxieties, it is important to provide information concerning ill-fated situations that is suitable for age among other things like emotional/physical support and re-assuring words.
The Education Ministry has actively participated through its network which includes more than 3,400 educational psychologists and 7,500 advisers as far as support is concerned.
These initiatives involve increased counseling hours for children evacuated from affected areas and psychological training for teachers and parents.
In order to support the educator community, their workload has been eased through mental health programs in schools.
Dr. Friedman clarified the distinction between trauma and coping with distress on a broader societal level.
Though there have been traumatic events, the impact varies as per personal resilience and coping mechanisms.
Responses of individuals are shaped by elements like inner strength, family-based safeguards, workplace environment, or openness to assistance.
Efforts are underway to provide adequate backing for mental health practitioners because they are also overwhelmed.
Activities include regular seminars that refresh their knowledge base and create a community of psychologists for them since they are instrumental in helping others.
Therefore, hope and resilience have been recognized as a cooperative venture requiring individual and collective efforts in the midst of incessant conflicts.
Thus, Dr. Friedman stressed the need for a united force in order to reframe the current unrest as temporary so as to ensure positive energy among people.
Henceforth, it is necessary to consider a holistic approach due to the scale of the present crisis that involves various psychological support systems, an involved community, and personal survival strategies.
What is needed is a mix of interconnected measures that can adequately deal with multifaceted problems facing us today.
To reduce the psycho-social toll of these troubled times on children and caretakers who often exhibit resilience.
Programs encouraging survival should reflect an informed understanding of these intricate needs.