A new article highlights the impact of caffeine on brain structure
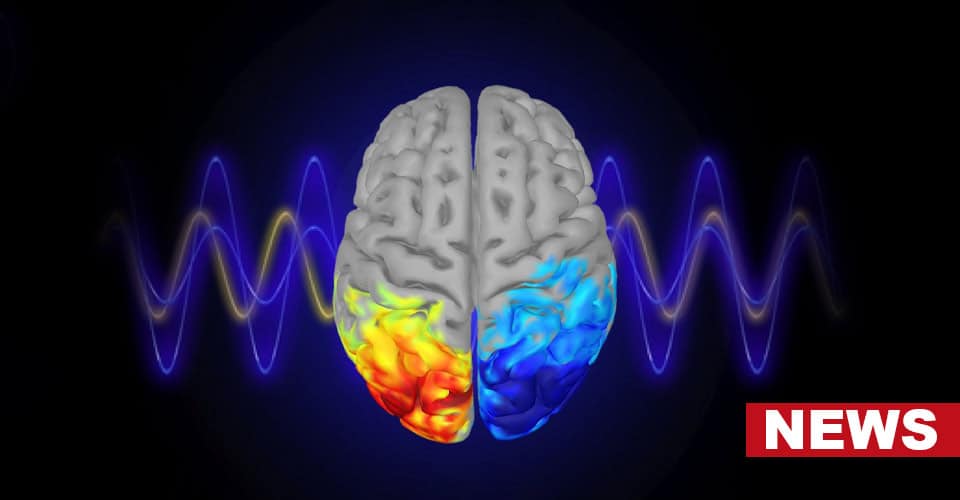
Caffeine may increase the severity of chronic sleep deprivation’s detrimental effects on grey matter in the brain, according to a recent study published in Scientific Reports. In fact, those who consumed caffeinated coffee during periods of restricted sleep experienced greater decreases in grey matter than those who did not indulge in it.
The research and its background
Caffeinated coffee is the most common psychoactive substance globally that is used to decrease fatigue and lessen cognitive impairments related to sleep loss. Nevertheless, it has been shown that acute sleep deprivation and regular coffee intake can lead to reductions in gray matter volume, an important component of the brain responsible for processing information and regulating cognitive functions.
Background: Key Findings
This study was conducted by Yu-Shiuan Lin (first author) University Psychiatric Clinics Basel; David Elmenhorst (senior author) Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine at Forschungszentrum Jülich; Germany. They aimed at investigating the interactions between daily coffee intake and chronic sleep restriction. More specifically, they wanted to establish whether or not taking coffee during instances of lack-of-sleep could further reduce the size of grey matter.
Research Methodology: Controlled Experiment
The experiment involved 36 healthy adults divided into two groups: one drinking caffeinated coffee (CAFF group) while the other drank decaffeinated coffee (DECAF group). Participants went through a nine-day controlled laboratory environment with an adaptation day followed by two baseline days 8-hour night-time sleeps each per night, five days under chronic sleep deprivation conditions(5 hours sleeping time each night) before finishing off with one recovery day with 8-hours’ night time sleep.
During this period of chronic sleep restriction phase, which lasted for several days only consuming 200mg caffeine in morning, 100mg afternoon for CAFF group but equivalent volumes were administrated as Decaffeinated coffee to DECAF group. There were three time points at which the subjects had MRI and PET scans, namely after the baseline days, during chronic sleep deprivation and recovery day. Caffeine levels in saliva were monitored through regular collection of samples.
Key Findings: Caffeine and Grey Matter Volume
The researchers observed considerable variations in the size of grey matter among the two groups. After undergoing a few days of insufficient sleep, individuals from DECAF group experienced increased grey matter amounts mainly on their prefrontal cortex, temporal occipital cortex or thalamus hence signaling for potential compensatory effects to prevent loss of sleep.
On the other hand, CAFF group participants indicated that caffeinated coffee might have inhibited brain’s compensatory mechanisms against sleep loss since they showed a reduction in gray matter volume within these regions. The research also found out that people with lower baseline adenosine receptor availability experienced more substantial declines in gray matter volume while under caffeine influence during inadequate sleep.
Adenosine Receptor Insights
Finally, another aspect investigated was the role played by adenosine system especially A1-receptor availability concerning how the brain responds to caffeinated coffee and lack-of-sleep situations. In particular, Adenosine A1 receptors control neural activity and facilitate sleeping whereas caffeinated coffee is an antagonist binding to these receptors thereby causing attentiveness as well as fighting off drowsiness.
Receptors’ availability had been found being higher than those who took coffee had less impact on grey matter according to researchers. For example, most grey matter changes recovered after recovery sleep and around 30-hour caffeine withdrawal except increased volume in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (associated with sleep restriction) and decreased volume in thalamus (associated with coffee intake).
CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH
The study finally discovered that brain plasticity reduction brought on by sleep deprivation can be intervened by caffeine intake, which has a complex effect on grey matter. This research provides insight but also has limitations like small sample size and narrow selection criteria for participants.
Future studies may go further to employ advanced imaging techniques in determining specific variations of gray matter as well as the wider implications of caffeine’s effects on brain structure and cognitive function.
Yu-Shiuan Lin, Denise Lange, Diego Manuel Baur, Anna Foerges, Congying Chu, Changhong Li, Eva-Maria Elmenhorst, Bernd Neumaier, Andreas Bauer, Daniel Aeschbach, Hans-Peter Landolt and David Elmenhorst are the authors of the paper entitled “Repeated caffeine intake suppresses cerebral grey matter responses to chronic sleep restriction in an A1 adenosine receptor-dependent manner: a double-blind randomized controlled study with PET-MRI.”