Sexual masochism disorder (SMD) is characterised by repeated and strong sexual arousal in reaction to moderate or severe pain, suffering, or humiliation. It becomes a clinical disorder when the impulses begin to interfere with important aspects of one’s life, such as relationships, jobs, and careers. This article will go through the many aspects of this condition, such as symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment choices.
What Is Sexual Masochism Disorder?
Sexual masochism disorder is a condition where individuals use sexual fantasies, urges, or behaviors defined by the act of being humiliated, beaten, or otherwise achieve sexual excitement and climax. These acts may be in the form of verbal humiliation or may involve being beaten, bound, or otherwise abused.
There are incidents where masochists may act out their fantasies on themselves by cutting or piercing their skin, or by burning themselves. Additionally, they may also seek a sadist partner who will enjoy inflicting pain or humiliation on others. Activities with a partner include bondage, spanking, and simulated rape.
Sadomasochistic fantasies and activities are common among consenting adults as in most of these cases, the humiliation and abuse are a part of their fantasy. The participants acknowledge the fact that the behavior is a “game,” where actual pain and injury is avoided.
However, a possibly dangerous, sometimes deadly, masochistic activity is autoerotic partial asphyxiation. In this disorder, the person restricts his/her breathing near the time or while orgasming to enhance the experience. Articles such as scarves, underwear, ropes, or nooses are used to choke themselves to enhance orgasm, however, accidental deaths can also occur.
Sexual masochism is also a form of paraphilia, however, most people who have masochistic interests do not meet clinical criteria for a paraphilic disorder as it requires that the person’s fantasies or intense urges cause clinically significant distress or impairment.
According to a study 1 Fisher KA, Marwaha R. Paraphilia. [Updated 2021 Mar 2]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554425/ , paraphilias are persistent and repetitive sexual interests, urges, fantasies, or behaviors marked by the involvement of objects, activities, or even situations that are unusual in nature. Although not innately disordered, a paraphilic disorder can develop if paraphilia invokes harm, distress, or functional impairment on the lives of the affected individual or others. In DSM-5, a total of eight Paraphilias are listed namely pedophilia, exhibitionism, voyeurism, sexual sadism, sexual masochism, frotteurism, fetishism, and transvestic fetishism.
Prevalence Of Sexual Masochism Disorder?
According to a study 2 Coluccia, A., Gabbrielli, M., Gualtieri, G., Ferretti, F., Pozza, A., & Fagiolini, A. (2016). Sexual masochism disorder with Asphyxiophilia: A deadly yet underrecognized disease. Case Reports in Psychiatry, 2016, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5474862 , the prevalence rate of sexual masochism disorder was between 1 to 5% across the US and Australian general population. In a Canadian study 3 Krueger, R. B. (2010). The DSM diagnostic criteria for sexual masochism. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 39(2), 346-356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-010-9613-4 , sadomasochistic sexual fantasies during sexual intercourse were reported close to 10% in men and a large percentage of females, ranging from 31 to 57%, were reported to have rape fantasies.
In a survey 4 Coluccia, A., Gabbrielli, M., Gualtieri, G., Ferretti, F., Pozza, A., & Fagiolini, A. (2016). Sexual Masochism Disorder with Asphyxiophilia: A Deadly yet Underrecognized Disease. Case reports in psychiatry, 2016, 5474862. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5474862 of sexual behaviour in the US involving 2026 respondents, it was observed that 4.8% of males and 2.1% of females reported ever having obtained sexual pleasure from inflicting pain and 2.5% of males and 4.6% of females from receiving pain. Additionally, a review of the literature 5 Critelli JW, Bivona JM. Women’s erotic rape fantasies: an evaluation of theory and research. J Sex Res. 2008 Jan-Mar;45(1):57-70. doi: 10.1080/00224490701808191. PMID: 18321031. on women’s rape fantasies reported that 31–57% of women had fantasies in which they were forced into sex against their will and that for 9–17% these were frequently experienced fantasies.
Causes Of Sexual Masochism Disorder
There are no exact causes or universally accepted theories defining the root cause of sexual masochism. However, experts have tried to link it with the presence of sexual paraphilias in general. It is believed that paraphilias originate due to suppressing sexual fantasies, thereby leading to forbidden sexual desires which only become stronger with time. However, when such sexual fantasies are finally acted upon, a person goes into a state of considerable distress or arousal and the masochistic behavior becomes inevitably linked to sexual behavior.
Additionally, factors like childhood trauma such as sexual abuse, or other notable childhood experiences may also lead to the development of this paraphilic disorder. Some also think may be caused by differences in the brain or nervous system. Factors like sexual impulsivity and hypersexuality also change over time and with age and can play a vital role in the development of this disorder. While sexual masochism disorder mostly starts in early adulthood, masochistic fantasies can also occur during childhood.
Read More About Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder In Children Here
Symptoms Of Sexual Masochism Disorder
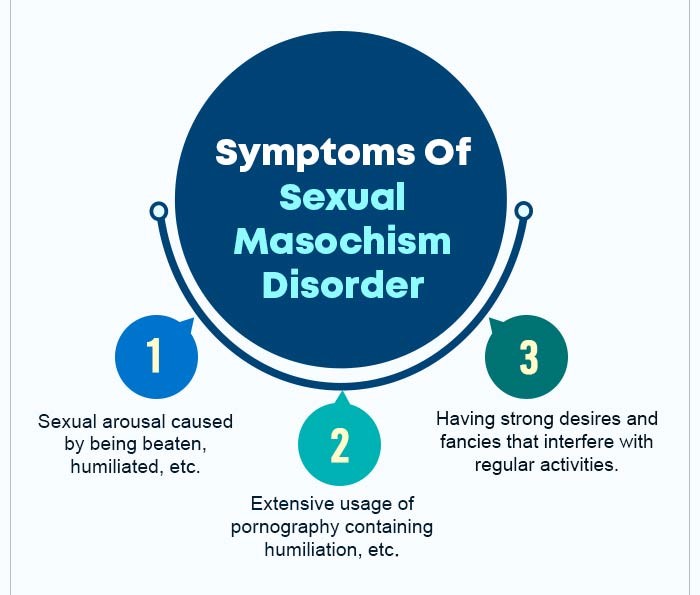
To be diagnosed with sexual masochism disorder, a person must exhibit the following symptoms for a period of at least six months. The following symptoms include:
- Experiencing intense sexual arousal after being beaten, humiliated, bound, or from some other form of suffering inflicted by the partner
- Having urges, fantasies, or actions that upset the person and cause severe problems in school, the workplace, or in relationships.
- Extensive use of pornography defined by the act of being beaten, humiliated, bound, or otherwise is also a feature connected to the disorder
Diagnosis Of Sexual Masochism Disorder
During the diagnosis of sexual masochism disorder, the primary healthcare provider will gather knowledge about the patient about his/her relationship and family history along with any substance abuse. As a basic protocol, the patient should be honest to his/her doctor as it is the only way to help the doctor to come with the best, suitable treatment plan. Additionally, the doctor will also talk about the visible symptoms, medical history, and accordingly suggest a few physical exams. He/she may be referred to as a mental health therapist for treatment.
According to the DSM-5 (2013), the main focus of the disorder revolves around sexual arousal induced by humiliation, being bound, bound, or made to suffer in some way. As with any other disorder, one must meet the following criteria as per DSM-5 to be diagnosed with sexual masochism disorder.
- Over a period of 6 months or longer, the individual should experience intense sexual arousal through actions such as humiliation, being beaten, or when hurt, as manifested by fantasies and behaviors.
- The fantasies and actions should cause significant distress or impairment in important areas of life, like at work or in one’s relationships.
Also, if an individual meets the DSM-5 criteria for sexual masochism disorder, it is also necessary to evaluate and specify the following.
- Does the Disorder Involve Asphyxiophilia? It means that the individual restricts his or her breathing in order to achieve the desired sexual arousal.
- Is He/She in a Controlled Environment? It means that the individual should be living in a setting that particularly restricts opportunities to engage in masochistic sexual behaviors.
- Is He/She in Full Remission? A condition where the individual has not experienced distress or impairment in significant areas of life for at least 5 years while in an uncontrolled environment.
Read More About DSM-5 Here
Treatment Of Sexual Masochism Disorder
It must be noted that treatment for sexual masochism disorder often turns out to be ineffective. Despite the fact, there are a few treatment options, mainly medication & therapy, that can help manage the disorder to a certain extent. Thus, if an individual is suffering from the concerned disorder, he/she may seek professional help to manage the symptoms for the same.
1. Psychotherapy
The main purpose of the treatment through therapy is to reveal and work through underlying causes of unwanted, distressful behaviors. For this purpose, cognitive-behavioral therapy or popularly known as CBT, is especially effective as it helps in modifying one’s thinking pattern and beliefs that may prevent engagement in harmful behavior.
It may also help one to learn new skills that may further enhance the importance of resisting sexual urges. The therapy is defined by the reconstruction of cognitive distortions through empathy training. Restructuring cognitive distortions involve rectifying any beliefs a patient has that may lead them to act on harmful thoughts.
According to a study 6 Kaplan, M. S., & Krueger, R. B. (2012). Cognitive-Behavioral Treatment of the Paraphilias. Please Wait… | Cloudflare. https://cdn.doctorsonly.co.il/2013/03/08_-Cognitive-behavioral-treatment.pdf , cognitive-behavioral therapy was and continues to remain an effective approach for the treatment of sex offenders and/or individuals with paraphilias. Its main treatment strategy of this therapy involves reducing inappropriate sexual arousal through a variety of techniques, including covert sensitization, satiation, fading, and systematic desensitization.
This approach also aims to intensify appropriate sexual arousal through techniques such as orgasmic reconditioning or fading. Additionally, there are other components of cognitive-behavioral treatment such as cognitive restructuring, social skills training, assertive skills training, addressing intimacy deficits, sexual education, enhancing empathy, sexual dysfunction treatment, personal victimization, relapse prevention, and diversity of adjunctive treatments which have been developed over the years.
Read More About Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Here
2. Medication
There are certain medications that may be used to decrease testosterone levels in order to reduce the occurrence of erections. Depot antiandrogen injections, for example, reduces libido, thereby decreasing masturbation, erections, and sexual fantasies. This is not a long-term solution, however, works particularly well in inpatient situations.
Additionally, antidepressant medications may be prescribed by the doctor to reduce the overall sex drive. While medication alone cannot resolve sexual masochism disorder, it can conquer a few symptoms such as hypersexual desires and anxiety that may prevent the treatment. Medication should stop at the patient’s request when ‘out-of-control sexual masochism’ has been resolved.
Since not all sexually masochistic behaviors hold clinical significance, treatment is only provided when patients complain of distress related to their sexual behavior.
Read More About Antidepressants Here
How Can Someone Overcome The Symptoms Of Sexual Masochism Disorder?
Apart from seeking professional help, an individual can himself/herself take a few steps to control the sexual urges to overcome the symptoms. He/she may:
- Avoid using illegal drugs or alcohol as such elements can make the symptoms worse
- Follow the exact directions as mentioned by the doctor for prescribed medicine
- Ask the healthcare provider whether the symptoms are getting worse or if he/she is having trouble dealing with them
Our Final Words
Is it right to label this habit as a mental illness? Some people may not be completely satisfied with their sex lives and they may look for adventures to add a spark to their sex lives through new experiments. Thus, some newcomers to sexual masochism may not be masochists in a true sense.
Sexual masochism has been found to fit otherwise normal, healthy individuals. It should be considered a disorder if it becomes an addiction and interferes with the person’s general level of functioning. Timely treatment may help to reduce the symptoms, however, it is not a completely curable condition.