The treatment of paranoid schizophrenia involves a holistic approach aimed at addressing the specific needs of individuals and facilitating their recovery from the challenges they encounter, while also providing essential support for their caregivers.
Treating Paranoid Schizophrenia
Treatment for paranoid schizophrenia primarily focuses 1 Krzystanek, M., Krysta, K., & Skałacka, K. (2017). Treatment Compliance in the Long-Term Paranoid Schizophrenia Telemedicine Study. Journal of technology in behavioral science, 2(2), 84–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-017-0016-4 on managing and alleviating symptoms to promote independent functioning and improve the overall quality of life.
Overcoming the obstacles presented by paranoid schizophrenia requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted treatment approach that incorporates various interventions and support programs, along with the unwavering dedication of caregivers to enhance both physical and psychological well-being.
It is essential for patients and caregivers to maintain realistic expectations and exercise patience, as the paranoid schizophrenia treatment is often a lifelong process. Consistency and commitment to treatment are vital, even when the patient starts experiencing improvements as stopping medications suddenly can lead to relapse or worsen 2 Pinkham, A. E., Harvey, P. D., & Penn, D. L. (2016). PARANOID INDIVIDUALS WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA SHOW GREATER SOCIAL COGNITIVE BIAS AND WORSE SOCIAL FUNCTIONING THAN NON-PARANOID INDIVIDUALS WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA. Schizophrenia research. Cognition, 3, 33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scog.2015.11.002 the symptoms.
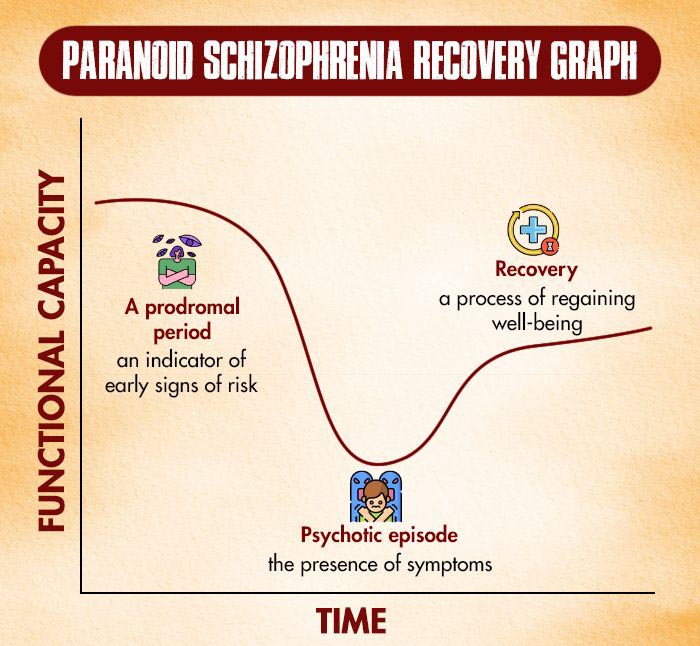
Different Treatment Measures for Paranoid Schizophrenia
Paranoid schizophrenia is a complex mental health 3 Lloyd, J., Lloyd, H., Fitzpatrick, R., & Peters, M. (2017). Treatment outcomes in schizophrenia: qualitative study of the views of family carers. BMC psychiatry, 17(1), 266. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-017-1418-8 condition that requires a multifaceted treatment approach, such as:
1. Medication
Antipsychotic medications are prescribed 4 Toto, S., Grohmann, R., Bleich, S., Frieling, H., Maier, H. B., Greil, W., Cordes, J., Schmidt-Kraepelin, C., Kasper, S., Stübner, S., Degner, D., Druschky, K., Zindler, T., & Neyazi, A. (2019). Psychopharmacological Treatment of Schizophrenia Over Time in 30 908 Inpatients: Data From the AMSP Study. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology, 22(9), 560–573. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyz037 to manage symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia like hallucinations and delusions. The choice of medication depends on individual response, tolerability, and side effects. Close monitoring and dosage adjustments are often needed for optimal symptom control.
2. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy 5 Kart, A., Özdel, K., & Türkçapar, M. H. (2021). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Treatment of Schizophrenia. Noro psikiyatri arsivi, 58(Suppl 1), S61–S65. https://doi.org/10.29399/npa.27418 (CBT), is often employed to help individuals with symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia, such as distorted thoughts, and improve problem-solving skills.
Also, electroconvulsive therapy 6 Phutane, V. H., Thirthalli, J., Kesavan, M., Kumar, N. C., & Gangadhar, B. N. (2011). Why do we prescribe ECT to schizophrenia patients?. Indian journal of psychiatry, 53(2), 149–151. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.82544 (ECT) has a positive impact on brain chemistry and can help alleviate severe symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Read More About Psychotherapy Here
3. Hospitalization
If medications and therapy are ineffective 7 Chen, E., Bazargan-Hejazi, S., Ani, C., Hindman, D., Pan, D., Ebrahim, G., Shirazi, A., & Banta, J. E. (2021). Schizophrenia hospitalization in the US 2005-2014: Examination of trends in demographics, length of stay, and cost. Medicine, 100(15), e25206. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000025206 in managing delusions and hallucinations, hospitalization may be recommended to provide the best treatment for paranoid schizophrenia. It may also be necessary if the symptoms become severe and there is a risk of harm to oneself or others. Hospitalization may be suggested for individuals who are unable to care for themselves or meet basic needs.
Overcoming Paranoid Schizophrenia
Here are some essential aspects 8 Ganguly, P., Soliman, A., & Moustafa, A. A. (2018). Holistic Management of Schizophrenia Symptoms Using Pharmacological and Non-pharmacological Treatment. Frontiers in public health, 6, 166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00166 of overcoming paranoid schizophrenia:
- Lean on your understanding family for emotional support, assistance with medication management, and a nurturing environment for your healing.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management to improve your overall well-being.
- Participate in vocational training programs or educational courses for occupational growth to build job-specific skills or problem-solving abilities.
- Connect with support groups, peers, and mental health organizations to share experiences and gain valuable insights from others facing similar challenges.
- Participate in social events and activities to foster connections, reduce isolation, and enhance your social well-being.
- Identify potential triggers that may intensify the symptoms and develop strategies to manage them.
- Cultivate a sense of self-worth and confidence by recognizing your achievements and celebrating personal growth.
Takeaway
Paranoid schizophrenia treatment involves a comprehensive approach including medication management, therapy, and support from healthcare professionals and loved ones. It is essential to work closely with medical professionals to get the right treatment support that effectively manages symptoms.
At A Glance
- Treatment for schizophrenia with paranoia can be a lifelong process.
- Treatment for paranoid schizophrenia primarily focuses on managing and relieving the symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia.
- Paranoid schizophrenia treatment includes approaches like medication, psychotherapy, and hospitalization.
- It is essential to work closely with medical professionals to find the right medication and dosage.
- Essential aspects of overcoming paranoid schizophrenia are family support, a healthy lifestyle, self-care activities, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best treatment for paranoid schizophrenia?
Antipsychotic medications are typically the first-line treatment prescribed to address the symptoms of an acute episode of paranoid schizophrenia.
2. Is paranoid schizophrenia hard to treat?
Treating paranoid schizophrenia can be challenging due to its complex symptoms. However, with comprehensive treatment, individuals can achieve significant improvements.
3. Does paranoid schizophrenia get worse with age?
Schizophrenia generally does not improve with age. The symptoms of schizophrenia may either worsen over time or remain stable for some individuals.