Mental illness is a complex and diverse category of conditions that, significantly affects the thoughts, emotions, and behaviors of those who suffer. Understanding what is mental illness is essential for reducing stigma and providing effective support and treatment for mental illness.
What Is Mental Illness?
Mental illness refers to a range of conditions 1 Malla, A., Joober, R., & Garcia, A. (2015). “Mental illness is like any other medical illness”: a critical examination of the statement and its impact on patient care and society. Journal of psychiatry & neuroscience : JPN, 40(3), 147–150. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.150099 that affect a person’s thoughts, emotions, behavior, and overall mental well-being.
The understanding of what is mental illness has evolved. Historically, mental illness was often misunderstood and stigmatized. It was not until the late 19th-early 20th centuries that advancements in psychology, psychiatry, and neuroscience changed the notions of mental illness. Since then, efforts to reduce stigma and increase access to treatment and care have continued to evolve.
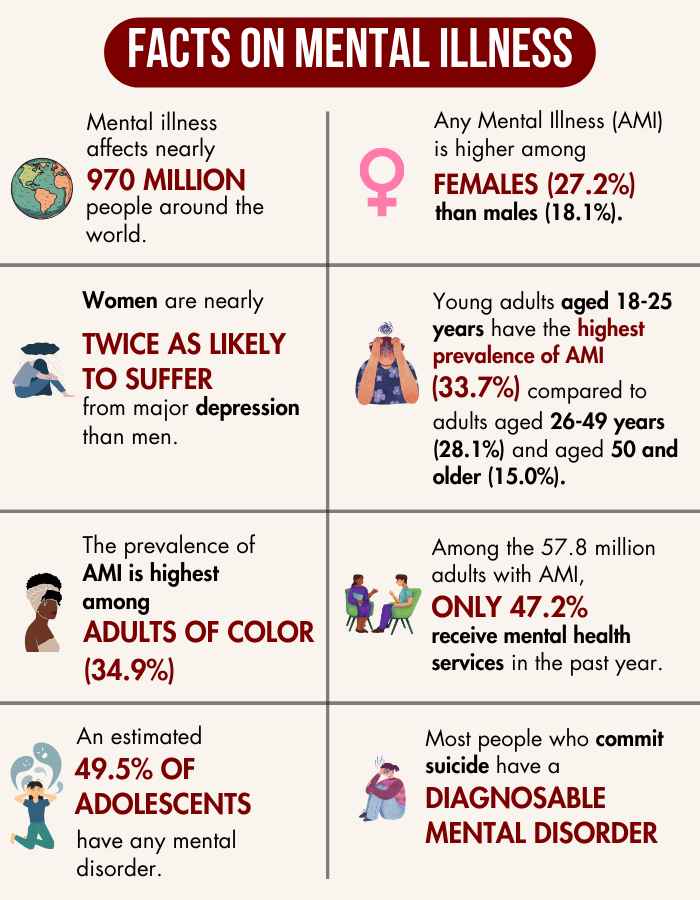
Today, “mental illness” has transitioned into “mental health disorder” and is now widely recognized as encompassing significant medical and treatable conditions 2 Galderisi, S., Heinz, A., Kastrup, M., Beezhold, J., & Sartorius, N. (2015). Toward a new definition of mental health. World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA), 14(2), 231–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20231 . It constitutes a public health issue affecting nearly 970 million people around the world.
Certain common types 3 National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (UK). (2011). COMMON MENTAL HEALTH DISORDERS. Nih.gov; British Psychological Society. Available From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92254/ of mental illness in children and adults are recognized and it is acknowledged that each condition is characterized by distinct symptoms and challenges. These include depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, etc.
Mental Illness In Cinema
Our understanding of what is mental illness comes from cinematic representation of mental health disorders like depression, psychosis, etc. Films like A Beautiful Mind (2001), Black Swan (2010), or The Perks Of Being A Wallflower (2012) have been praised over the years for renegotiating the concepts of mental illness and mental health.
However, certain films like The Shinning (1980) or Joker (2019) have been accused of perpetrating the negative stereotypes associated with mental illness and mentally ill individuals.
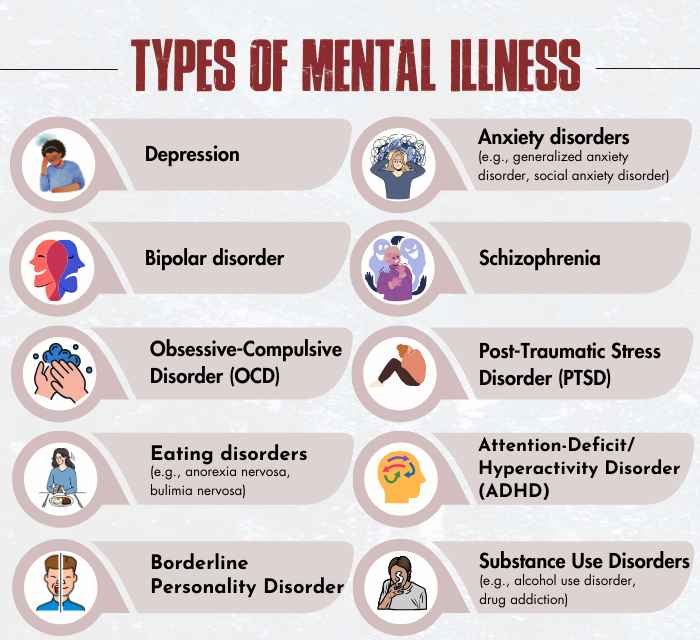
The Signs And Symptoms Of Mental Illness
Research 4 Manderscheid, R. W., Ryff, C. D., Freeman, E. J., McKnight-Eily, L. R., Dhingra, S., & Strine, T. W. (2010). Evolving definitions of mental illness and wellness. Preventing chronic disease, 7(1), A19. attributes the common signs and symptoms of mental illness to the following:
- Mood swings and extreme emotions
- Social withdrawal and isolation
- Poor concentration and decision-making
- Sleep and appetite changes
- Unexplained physical symptoms
- Increased substance use
- Disturbed thinking
- Coping difficulties
- Heightened anxiety
- Self-harm or suicidal thoughts
Read More About Decision-Making Here

What Causes Mental Illness?
Experts attribute what causes mental illness in children and adults to the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors 5 NCBI. (2012). Information about Mental Illness and the Brain. Nih.gov; National Institutes of Health (US). Available From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK20369/ :
- Family history and genetic predisposition.
- Neuro-developmental factors, including brain chemistry and structure.
- Traumatic experiences, such as abuse or loss.
- Stress, life events, and lifestyle choices.
- Substance abuse and certain medical conditions.
- Cultural and societal influences.
Read More About Stress Here
The Impact Of Mental Illness On Mental Health
The impact of mental illness on mental health in individuals can be severe, disrupting 6 Defar, S., Abraham, Y., Reta, Y., Deribe, B., Jisso, M., Yeheyis, T., Kebede, K. M., Beyene, B., & Ayalew, M. (2023). Health related quality of life among people with mental illness: The role of socio-clinical characteristics and level of functional disability. Frontiers in public health, 11, 1134032. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1134032 their emotional, cognitive, and behavioral well-being. It often leads to persistent and distressing symptoms like depression, anxiety, mood swings, or hallucinations, which can erode one’s sense of self and overall quality of life. The distress and impairment caused by mental illness in children and adults can strain relationships, hinder daily functioning, and even lead to physical health problems.
Moreover, it may contribute to feelings of isolation, shame, and stigma, further exacerbating the mental health challenges individuals face. Additionally, untreated or poorly managed mental illness can create a vicious cycle, where symptoms worsen over time, making it increasingly challenging to recover.
Read More About Depression Here
How To Diagnose Mental Illness
Mental illness is diagnosed through a combination of standardized tools and clinical assessments 7 Stein, D. J., Shoptaw, S. J., Vigo, D. V., Lund, C., Cuijpers, P., Bantjes, J., Sartorius, N., & Maj, M. (2022). Psychiatric diagnosis and treatment in the 21st century: paradigm shifts versus incremental integration. World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA), 21(3), 393–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20998 . The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) provide guidelines and criteria for mental health diagnoses. Mental health professionals conduct clinical interviews and psychological assessments (using scales like the Beck Depression Inventory or GAD-7), as well as observe behavior, to gather diagnostic information about what causes mental illness.
In some cases, neuroimaging and lab tests may be employed to rule out underlying medical conditions. Cultural competence is essential in considering cultural factors that influence symptom expression, and the methods on how to diagnose mental illness. These may evolve, requiring ongoing assessment and treatment adjustments.
Treatment For Mental Illness
Treatment for mental illness typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support 8 Harvey, A. G., & Gumport, N. B. (2015). Evidence-based psychological treatments for mental disorders: modifiable barriers to access and possible solutions. Behaviour research and therapy, 68, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2015.02.004 . Psychotherapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy [CBT] or talk therapy) helps individuals manage signs and symptoms of mental illness and develop measures on how to cope with mental illness.
Medications like antidepressants or mood stabilizers may be prescribed when necessary. Lifestyle modifications, including exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can also support recovery.

How To Cope With Mental Illness
Consider the following measures 9 Biringer, E., Davidson, L., Sundfør, B., Lier, H. Ø., & Borg, M. (2016). Coping with mental health issues: subjective experiences of self-help and helpful contextual factors at the start of mental health treatment. Journal of mental health (Abingdon, England), 25(1), 23–27. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638237.2015.1078883 on how to cope with mental illness:
- Seek professional help from therapists, counselors, or psychiatrists.
- Follow prescribed treatment plans, including medications and therapy.
- Develop a support system by confiding in friends and family.
- Educate yourself about your condition to understand better and manage it.
- Practice stress management techniques like mindfulness or meditation.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle through exercise and a balanced diet.
- Set realistic goals and break tasks into manageable steps.
- Avoid substance abuse, as it can worsen symptoms.
- Engage in hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation.
- Consider joining support groups or online communities for shared experiences and advice.
Read More About Meditation Here
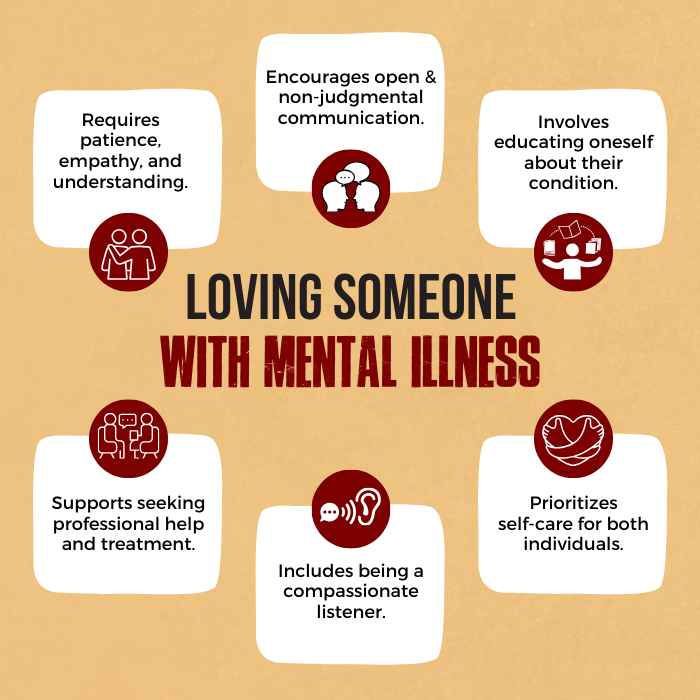
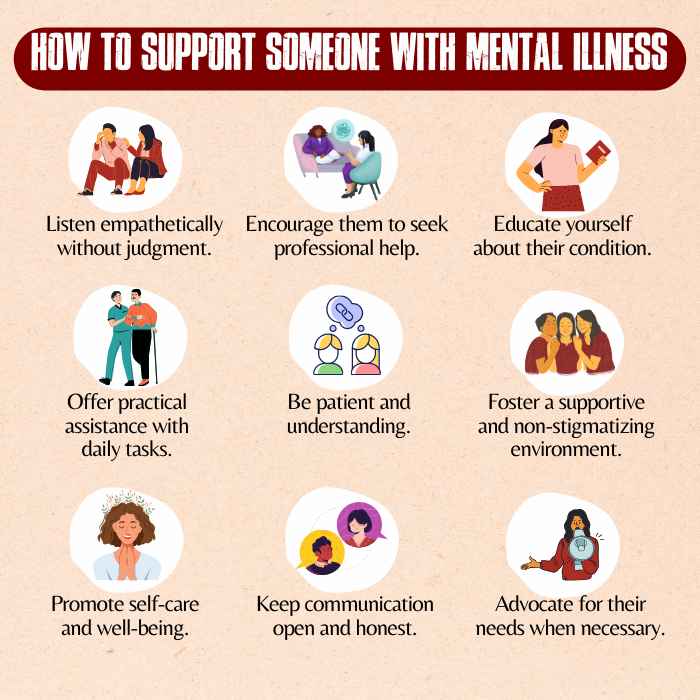
Supporting And Loving Someone With Mental Illness
Social support networks, peer groups, and community resources are essential components of the treatment process 10 Chronister, J., Fitzgerald, S., & Chou, C. C. (2021). The meaning of social support for persons with serious mental illness: A family member perspective. Rehabilitation psychology, 66(1), 87–101. https://doi.org/10.1037/rep0000369 , contributing to improved mental health and overall well-being. In addition, when supporting and loving someone with mental illness, practicing patience, empathy, and open communication is crucial.
Educating oneself about what is mental illness (or their condition), offering non-judgmental emotional support, encouraging professional help, and being a compassionate listener are key aspects. Establishing a robust support system and prioritizing self-care are equally vital for both the individual with mental illness and their loved ones to navigate challenges and enhance well-being collectively.
Developing Mental Health Awareness
Developing mental health awareness involves educating oneself and others 11 Singh, V., Kumar, A., & Gupta, S. (2022). Mental Health Prevention and Promotion-A Narrative Review. Frontiers in psychiatry, 13, 898009. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.898009 about the importance of mental well-being, recognizing the signs of mental health challenges, reducing stigma, and fostering a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and discussing their mental health. It also involves promoting self-care and mental health hygiene practices to enhance overall psychological resilience and well-being in society.
Takeaway
The significance of understanding what is mental illness in children and adults cannot be overstated. It is not merely a matter of recognizing its prevalence; rather, it is about creating a more compassionate and inclusive society that embraces individuals dealing with mental health challenges.
Through increased awareness, we can break down the barriers of stigma, encourage open dialogue, and ensure that those in need receive the necessary care and support. Ultimately, by fostering a deeper understanding of mental illness, we empower individuals to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives, promoting well-being for all.
At A Glance
- Mental illness is a complex condition that affects thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
- The impact of mental illness can be felt in our personal and professional lives.
- Understanding what is mental illness helps check its mental health consequences in the long run.
- Measures on how to diagnose mental illness involve standardized tools and interviews.
- Treatment for mental illness includes therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
- Measures on how to cope with mental illness involve seeking help and practicing self-care.
- Supporting and loving someone with mental illness requires empathy, while mental health awareness reduces stigma and promotes well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can people get over mental illness without medication?
Some can recover from mental illness without medication, but it varies.
2. Can individuals with chronic mental illness recover?
Individuals with chronic mental illness can often lead fulfilling lives with appropriate treatment, support, and management strategies, although complete recovery may not always be possible.
3. What is the most curable mental illness?
The concept of the “most curable” mental illness is subjective and depends on various factors, including individual differences, available treatments, and the severity of the illness.
4. Is mental illness the same as madness?
Mental illness is distinct from the colloquial term “madness.” Mental illness refers to a wide range of conditions that affect thoughts, emotions, and behavior, while “madness” is a stigmatizing term often associated with severe mental health crises or stereotypes.