Evolutionary psychology explores how our ancestral past has shaped our psychological traits and behaviors. It provides valuable insights into understanding mental health by illuminating the connections between our evolved mechanisms and modern-day challenges—guiding the development of interventions to improve mental well-being.
What Is Evolutionary Psychology?
Evolutionary psychology delves into the origins of human behavior and cognition 1 Egeland J. (2023). Evolutionary Psychology and Normal Science: in Search of a Unifying Research Program. Integrative psychological & behavioral science, 57(2), 390–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-022-09736-x , tracing them back to the adaptive advantages they offered our ancestors in survival and reproduction. It is based on Darwin’s theory of evolution published in 1859, that argued that evolution acted on patterns of behavior as well as the anatomy and physiology of the body.
By exploring how natural selection shaped our cognitive mechanisms, research into what is evolutionary psychology claims our mental processes are purposeful products of evolution. These are honed to solve both the challenges of our ancestral environments and modern-day settings.
Evolutionary Psychology Examples
Common 2 Ramachandran, V. S., & Jalal, B. (2017). The Evolutionary Psychology of Envy and Jealousy. Frontiers in psychology, 8, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01619 evolutionary psychology examples include:
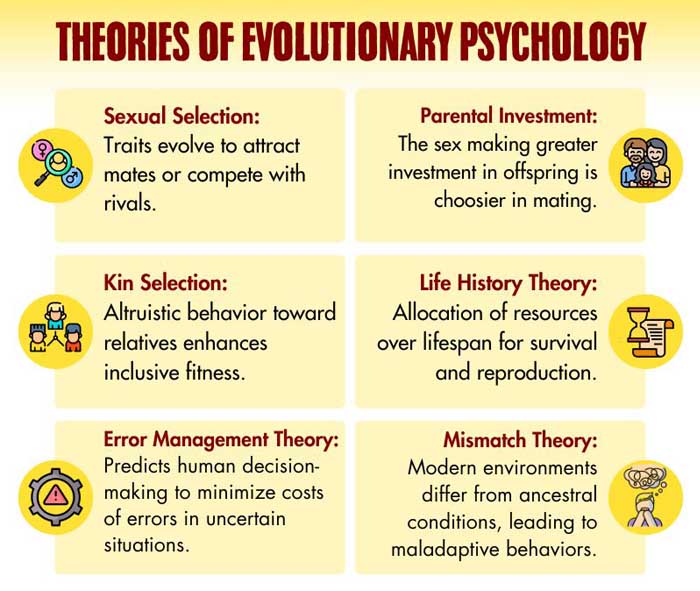
- Mate Selection: Preferring traits indicating genetic fitness, like facial attractiveness.
- Parental Investment: Varied parenting strategies based on reproductive investment.
- Fear of Snakes: Ancestral fear due to historical danger, leading to quick fear responses.
- Sexual Jealousy: Emotions to prevent mate desertion.
- Food Preferences: Cravings for scarce energy sources like fatty, sugary foods.
- Altruism: Helping kin for increased inclusive fitness.
- Fears of Heights: Fear as a protective mechanism against falls.
Read More About Altruism Here

Evolutionary Factors That Affect Mental Health
Certain 3 Cosmides, L., & Tooby, J. (2013). Evolutionary psychology: new perspectives on cognition and motivation. Annual review of psychology, 64, 201–229. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.121208.131628 evolutionary factors that affect mental health include:
- Genetic predispositions
- Natural selection pressures
- Evolutionary mismatch (misalignment with modern environment)
- Adaptive behaviors from ancestors
- Evolution of stress responses
- Social hierarchies and their impact
- Development of emotion regulation
- Evolution of cognitive biases and heuristics
- Impact of early childhood experiences on later mental health
- Evolution of social support systems.
Read More About Cognitive Bias Here
Evolutionary Psychology And Mental Health
Evolutionary psychology and mental health are intricately related, providing a framework for understanding how our ancestral history shapes mental functioning 4 Shackelford, T. K., & Liddle, J. R. (2014). Understanding the mind from an evolutionary perspective: an overview of evolutionary psychology. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Cognitive science, 5(3), 247–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.1281 today. It suggests that many mental health challenges stem from evolutionary mismatches, where our modern environment differs significantly from the conditions under which our ancestors evolved. For example, anxiety might be an adaptive response to potential threats in the wild, but in today’s world of constant stimuli and stressors, it can become maladaptive.
Additionally, evolutionary psychology emphasizes the importance of adaptive behaviors 5 Han, W., & Chen, B. B. (2020). An evolutionary life history approach to understanding mental health. General psychiatry, 33(6), e100113. https://doi.org/10.1136/gpsych-2019-100113 that might have been beneficial in the past but are less helpful in modern contexts. For instance, certain cognitive biases or emotional responses that were once advantageous for survival can now contribute to conditions like depression or anxiety disorders.
How Does Evolutionary Psychology Explain Mental Illness?
Evolutionary psychology and mental health have often leaned on to each other to explain the development of several mental health disorders 6 Confer, J. C., Easton, J. A., Fleischman, D. S., Goetz, C. D., Lewis, D. M., Perilloux, C., & Buss, D. M. (2010). Evolutionary psychology. Controversies, questions, prospects, and limitations. The American psychologist, 65(2), 110–126. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018413 like:
- Anxiety Disorders: Once an adaptive response to ancestral threats, now maladaptive in modern stressors.
- Depressive Disorders: Possibly evolved to conserve energy during scarcity, now manifesting as clinical depression.
- PTSD: Originating as extreme reactions to past threats, now often maladaptive in safe environments.
- Eating Disorders: Rooted in ancestral adaptation to food scarcity, now harmful with food abundance 7 Nettersheim, J., Gerlach, G., Herpertz, S., Abed, R., Figueredo, A. J., & Brüne, M. (2018). Evolutionary Psychology of Eating Disorders: An Explorative Study in Patients With Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa. Frontiers in psychology, 9, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02122 .
- Substance Use Disorders: Originating from seeking substances for consciousness alteration, now leading to addiction.
- Neuro-developmental Disorders: Variations once beneficial in ancestral tasks, now challenging in modern contexts 8 Funkhouser E. (2021). Evolutionary psychology, learning, and belief signaling: design for natural and artificial systems. Synthese, 199(5-6), 14097–14119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-021-03412-0 .
Read More About PTSD Here
Application Of Evolutionary Psychology In Mental Healthcare
Application of evolutionary psychology in mental healthcare often entails 9 Bjorklund D. F. (2016). Incorporating Development Into Evolutionary Psychology: Evolved Probabilistic Cognitive Mechanisms. Evolutionary Psychology, 14(4), 1474704916670166. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474704916670166 :
- Reducing stigma by explaining mental health issues through evolutionary history.
- Tailoring interventions 10 Abed, R., Brüne, M., & Wilson, D. R. (2019). The role of the evolutionary approach in psychiatry. World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA), 18(3), 370–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20688 to align with evolved stress responses.
- Developing effective treatments targeting root causes, not just symptoms.
- Helping individuals understand and cope with their mental health challenges.
- Enhancing therapy by considering how ancestral behaviors manifest in modern context.
Takeaway
Evolutionary psychology offers valuable insights into the origins of mental health challenges and provides a framework for developing interventions that better align with our evolved mental mechanisms. By understanding how our ancestral past influences present-day mental health, we can tailor treatments to address root causes effectively, ultimately improving well-being in the complex and rapidly changing modern world.
At A Glance
- Evolutionary psychology explores how our ancestral past shapes psychological traits.
- What is evolutionary psychology connects evolved mechanisms to modern mental health challenges.
- Evolutionary psychology examples include mate selection, fears (like heights), and food preferences.
- Evolutionary factors that affect mental health include genetics, stress responses, and social hierarchies.
- The link between evolutionary psychology and mental health explains mental illnesses as evolutionary mismatches.
- Evolutionary psychology helps develop treatments by addressing the evolutionary causes of mental health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How Do Evolutionary Psychologists Work?
Evolutionary psychologists study how human behavior and cognition have been shaped by natural selection over time.
2. How Does Evolutionary Psychology Affect Human Behavior?
Evolutionary psychology suggests that many human behaviors are adaptations to the challenges our ancestors faced.
3. Why Is Evolutionary Psychology Useful?
Evolutionary psychology is useful for understanding the origins of human behavior, cognition, and emotions in an evolutionary context.