Dissociative Trance Disorder is a condition marked by a temporary change in consciousness, a loss of the usual sense of personal identity, a restricted awareness of one’s surroundings, and repetitive behaviors or movements that occur outside of one’s control.
What Is Dissociative Trance Disorder?
Dissociative Trance Disorder refers to a condition where an individual undergoes an involuntary detachment from reality, accompanied by a temporary shift in consciousness that disrupts normal daily functioning. This condition is also referred to as possession trance disorder or trance and possession disorder (TPD).
The person suffering from this condition feels overwhelmed by paranormal experiences. One study 1 Ferracuti, S., Sacco, R., & Lazzari, R. (1996). Dissociative trance disorder: clinical and Rorschach findings in ten persons reporting demon possession and treated by exorcism. Journal of personality assessment, 66(3), 525–539. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa6603_4 suggested that despite claiming that they were being possessed by a demon, they managed to maintain normal social functioning. Trance and possession disorders are defined by clinical psychiatry as states characterised by “a transient loss of personal identity and complete knowledge of one’s surroundings”. The International Classification of Diseases 2 The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders Diagnostic criteria for research. (n.d.). WHO | World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/GRNBOOK.pdf (ICD 10) classified this condition as a “type of dissociative disorder”. Dissociative disorder refers to the loss of normal integrative functions of the mind that affects memory, consciousness, and identity. The dissociative disorder manifests into different phenomenons such as amnesia, trance, and multiple personality disorder.
The first issue with this disease is obtaining a mental diagnosis, as dissociative trance disorder exhibits cross-cultural diversity that is difficult to identify without assessment. Most cultures have “spirit possession beliefs” 3 Bhavsar, V., Ventriglio, A. and Bhugra, D. (2016), Dissociative trance and spirit possession: Challenges for cultures in transition. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci., 70: 551-559. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12425 for people with this disorder. In social sciences, possession refers to the seizure of one’s spirit by another. In order to understand the prevalence of this condition one must accept that there is “really” something called “dissociative trance disorder”.
For people who were studied under this diagnostic criteria, some of them seemed to have severe impairment of reality testing while others had an extensive coping style. This group of persons who claimed to have been possessed by demons had a distinct clinical manifestation of a dissociative continuum, sharing some characteristics with dissociative identity disorder. However, the extent of studying this phenomenon is limited.
Trance disorder exclusively affects persons who have an odd involuntary incident that is neither a regular activity nor a widely accepted religious practise. To arrive at an accurate diagnosis, any organic reasons such as traumatic brain damage or epilepsy, as well as the effects of any psychoactive substance, must be ruled out.
There may be several factors that may contribute to developing this condition such as inherited genetic factors, socio-cultural factors, or economic factors. The first form of treatment is psychotherapy. Medications may be used in some instances where underlying conditions such as depression or anxiety are present. The diagnosis of this condition in western cultures is rare. This illness is still underdiagnosed in Western societies because to misunderstandings and cultural prejudices surrounding altered consciousness.
Signs And Symptoms Of Dissociative Trance Disorder
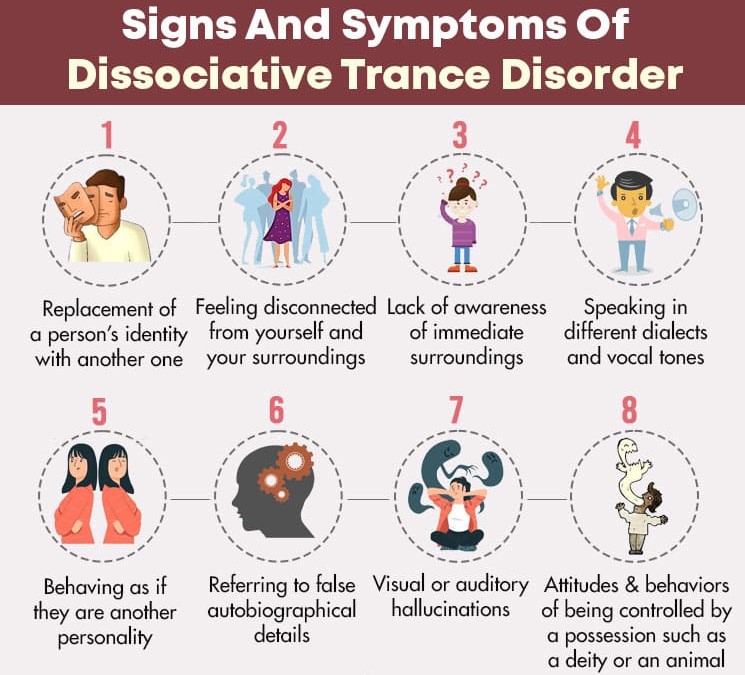
The following are the signs and symptoms of this condition:
- Replacement of a person’s identity with another one
- Feeling disconnected from yourself and your surroundings
- Lack of awareness of immediate surroundings
- Speaking in different dialects and vocal tones
- Behaving as if they are another personality
- Referring to false autobiographical details
- Visual or auditory hallucinations
- Attitudes and behaviors of being controlled by a possession such as a deity or an animal
Proposal Of Criteria For Dissociative Trance And Possession Disorder In DSM 5
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM 5) has proposed a method for diagnosing this condition.
A. Either (1) or (2)
- Trance Type: Temporary noticeable change in awareness or loss of conventional feeling of personal identity without replacement by an alternate identity connected with one of the following:
- Lack of awareness of immediate surroundings or unusually narrow and selective focusing on environmental stimuli.
- Repetitive or limited stereotypical behaviors and movements that are experienced or perceived beyond one’s control.
- Possession Type: A single or episodic alteration in the state of consciousness characterized by the replacement of customary sense of personal identity by the patient or his entourage as the spirit of an animal, a deceased individual, a deity, or a power, evidenced by at least one of the following:
- Determined behaviors, movements, speech, or attitudes that are experienced or recognized as being controlled by the possession agent.
- Visual or auditory hallucinations connected with the controlling agent.
B. The trance or possession state is not accepted as normal by the patient or his community and is usually not part of a cultural or religious practice
C. Trance or possession states occur involuntarily and produce clinically substantial distress or impairment in social, vocational, or other critical areas of functioning.
D. The trance or possession state does not occur during the course of a psychotic disorder (including mood disorder with psychotic features ), cases in which all symptoms cannot be accounted for by the presence of the external agent. This disorder is not due to the direct effects of a substance or a general medical affection.
Causes Of Dissociative Trance Disorder

The precise causes of this condition are unclear. However, there may be certain factors that contribute to this illness.
- Death of a relative, pathological mourning, conflicts over religious or cultural issues, tension from economic or social difficulties, altered group dynamics, a future engagement or marriage, sexuality or other societal taboos, feelings of guilt, or any other unspecified inner conflict are all examples of psychosocial stressors.
- Traumatic events such as sexual abuse or assault as a kid, war, or the untimely suicide of a relative
- Psychotic disorder or personality disorder, neurosis, or any other unique psychopathology are examples of psychiatric illnesses.
- Cultural influences based on a culturally imposed stereotype or acquired habit.
- Communication ideas that entail disadvantaged individuals expressing generic issues and exhibiting unsatisfied demands
- When the disease is shown for regeneration goals, the trance is said to be capable of bringing about social, economic, or psychological benefit, mediumistic powers, or extrasensory competences.
- Caused by the expression of histrionic personality, which includes an unresolved oedipal conflict and the danger of mass hysteria
Treatment For Dissociative Trance Disorder
According to one study 4 Ng, B. Y., & Chan, Y. H. (2004). Psychosocial stressors that precipitate dissociative trance disorder in Singapore. The Australian and New Zealand journal of psychiatry, 38(6), 426–432. https://doi.org/10.1080/j.1440-1614.2004.01379.x , psychotherapy is the primary kind of treatment that appears to bring some alleviation to the patient. Other sorts of therapy are employed to alleviate the symptoms of this condition.
1. Traditional Medicine
Traditional healers, faith healers, and shamans are frequently employed to treat persons who exhibit signs of dissociative trance or possession condition. According to research 5 Gaw, A. C., Ding, Q., Levine, R. E., & Gaw, H. (1998). The clinical characteristics of possession disorder among 20 Chinese patients in the Hebei province of China. Psychiatric services (Washington, D.C.), 49(3), 360–365. https://doi.org/10.1176/ps.49.3.360 , traditional medicine was employed by 30% of patients to treat this disease.
2. Exorcism
Exorcism is a religious or spiritual activity in which a priest exorcises demons or other spiritual beings from a person or location said to be possessed. This can be accomplished by making the creature take an oath to leave, completing a complex ceremony, or commanding it to leave in the name of a higher authority.
3. Psychotherapy
The most prevalent type of treatment is talk therapy or psychotherapy. This treatment assists the doctor in learning about the patient’s condition as well as his or her moods, feelings, thoughts, and actions. This assists a person in changing their behavior and overcoming challenges in the desired manner. Patients must express their sentiments and worries to a mental health expert so that the doctor may assist them with various coping techniques. Psychotherapy can assist in the elimination or management of problematic ideas that interfere with everyday functioning.
Read More About Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Here
4. Medications
Individuals suffering from this illness may also be provided medications. Antipsychotics and antidepressants are examples of such medications. According to a 1990 research 6 Witztum, E., Buchbinder, J. T., & van der Hart, O. (1990). Summoning a punishing angel: treatment of a depressed patient with dissociative features. Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic, 54(4), 524–537. , individuals who were taken antidepressants improved significantly. Anxiolytics are also administered and have been shown to provide some relief.
Read More About Antidepressants Here
5. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
This therapy is used to treat a variety of mental disorders. Electroconvulsive treatment entails sending a precisely regulated electric wave across the brain, which alters brain function. It is intended to alleviate severe depression and psychotic symptoms. In severe cases, people with DTD may be treated with ECT.
6. Hospitalization in a Psychiatric Ward
Psychiatric hospitals offer patients with a secure setting in which to heal via the use of a structured environment and therapy. A patient is admitted to a psychiatric ward for a certain period of time, which can range from a few days to a few months depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Dissociative Trance Disorder: An Underdiagnosed Condition
This is a common disorder that might be interpreted as a worldwide idiom of distress. Due to cultural prejudices, it is likely that it is underdiagnosed in Western nations. However, when the growing tide of migration is taken into account, the incidence may rise. More research is needed to determine the prevalence of this illness.. Due to cultural biases and misconceptions about altered states of consciousness in Western societies,the condition may still be underdiagnosed.
Dissociative Trance Disorder At A Glance
- Dissociative Trance Disorder involves a person experiencing an involuntary escape from reality and a temporary alteration in the state of consciousness that impairs the normal functioning of everyday life.
- The person suffering from this condition feels overwhelmed by paranormal experiences.
- There may be several factors that may contribute to developing this condition such as inherited genetic factors, socio-cultural factors, or economic factors.
- Psychotherapy is the primary kind of treatment that appears to bring some alleviation to the patient.
- This is a common disorder that might be interpreted as a worldwide idiom of distress.