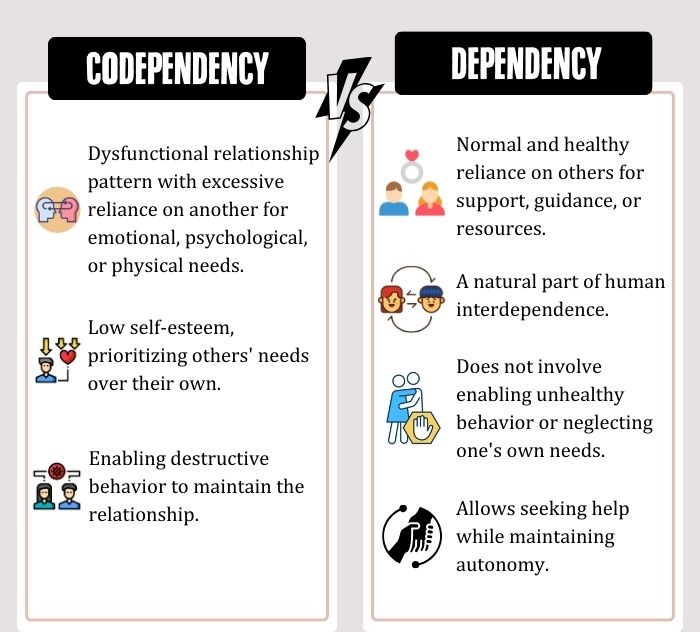
Codependency, in psychology, is a complex and pervasive behavioral pattern where one person becomes excessively reliant on another for emotional well-being and self-identity. Understanding the dynamics of codependency is crucial for promoting mental well-being and fostering healthier, more balanced social relationships.
What Is Codependency?
Codependency refers to a dysfunctional and unhealthy pattern of behavior 1 Morgan J. P., Jr (1991). What is codependency?. Journal of clinical psychology, 47(5), 720–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4679(199109)47:5<720::aid-jclp2270470515>3.0.co;2-5 in relationships, where one person excessively relies on another for their sense of self-worth, validation, and emotional well-being.
This codependent dynamic often occurs when one individual becomes overly dependent on fulfilling the needs and desires of another, often at the expense of their own needs and boundaries.
Codependent individuals tend to have low self-esteem, struggle with assertiveness, and have difficulty establishing healthy boundaries. This can lead to a cycle of enabling and dependency 2 Stafford L. L. (2001). Is codependency a meaningful concept?. Issues in mental health nursing, 22(3), 273–286. https://doi.org/10.1080/01612840121607 , where both parties reinforce the unhealthy dynamic.
An example of codependency can be seen in a romantic relationship where one partner constantly sacrifices their own needs and desires to cater to the other’s demands, even when it causes emotional distress or personal harm.
The codependent individual may feel an intense fear of rejection or abandonment, driving them to go to great lengths to keep the relationship intact, even if it means suppressing their true feelings or tolerating abusive behavior.
Prevalence Of Codependency
The prevalence of codependency varies widely depending on the population studied and the criteria used for assessment. It’s estimated that around 10% to 20% of the general population 3 Noriega, G., Ramos, L., Medina-Mora, M. E., & Villa, A. R. (2008). Prevalence of codependence in young women seeking primary health care and associated risk factors. The American journal of orthopsychiatry, 78(2), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.1037/0002-9432.78.2.199 may exhibit codependent tendencies.
Gender differences 4 Cowan, G., & Warren, L. W. (1994). Codependency and gender-stereotyped traits. Sex Roles, 30(9-10), 631–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01544667 in the prevalence of codependency suggest that it’s more commonly identified in women compared to men. This pattern may be influenced by societal and cultural factors that emphasize caretaking and emotional involvement, which are traits often associated with codependency.
However, it’s important to note that codependency can affect individuals of any gender, and the prevalence rates might vary in different populations and contexts.
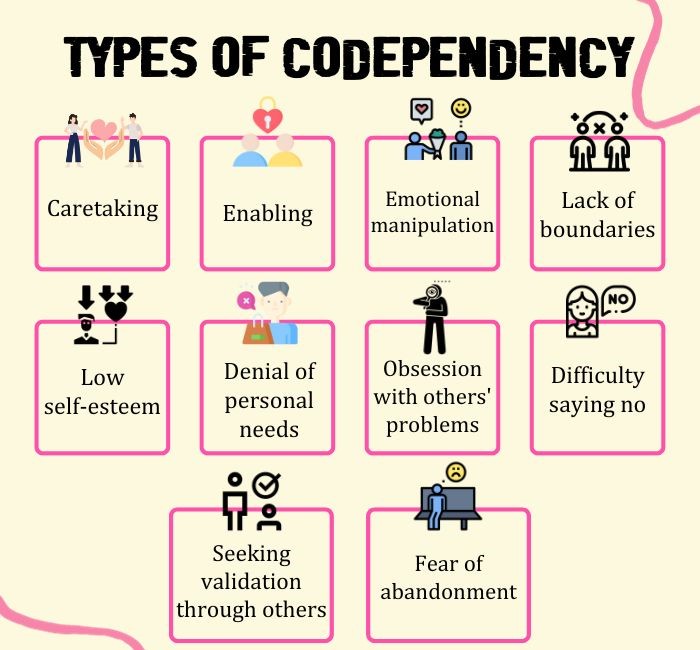
Signs Of Codependency
Common 5 Knapek, E., & Kuritárné Szabó, I. (2014). A kodependencia fogalma, tünetei és a kialakulásában szerepet játszó tényezők [The concept, the symptoms and the etiological factors of codependency]. Psychiatria Hungarica : A Magyar Pszichiatriai Tarsasag tudomanyos folyoirata, 29(1), 56–64. signs of codependency include:
- Difficulty setting boundaries
- Constantly seeking approval and validation from others
- Putting others’ needs above one’s own
- Fear of rejection or abandonment
- Overly controlling or care-taking behavior
- Difficulty expressing one’s feelings and needs
- Strong desire to please others, even at personal expense
- Feeling responsible for others’ emotions and actions
- Neglecting one’s own interests and hobbies
- Tendency to attract and maintain relationships with emotionally unavailable or abusive individuals.
What Causes Codependency ?
The different causes 6 Farmer S. A. (1999). Entitlement in codependency: developmental and therapeutic considerations. Journal of addictive diseases, 18(3), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1300/J069v18n03_06 for developing the signs of codependency include:
- Dysfunctional family dynamics or upbringing
- Childhood trauma or neglect
- Low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy
- Enabling behaviors in relationships
- Fear of abandonment or rejection
- Emotional dependency on others for validation
- Role models with codependent behaviors
- Substance abuse or addiction in the family
- Lack of healthy relationship boundaries
- Difficulty coping with emotions and stress
Read More About Addiction Here
Impact Of Codependency On Mental Health
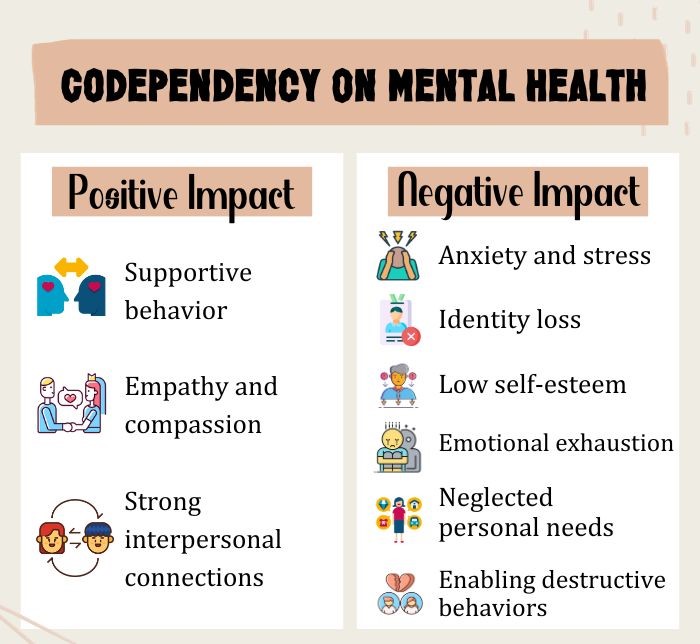
Codependency can have profound and detrimental effects 7 Vederhus, J. K., Kristensen, Ø., & Timko, C. (2019). How do psychological characteristics of family members affected by substance use influence quality of life?. Quality of life research : an international journal of quality of life aspects of treatment, care and rehabilitation, 28(8), 2161–2170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02169-x on an individual’s mental health and overall well-being:
- Focus on others’ needs neglects self, causing exhaustion, anxiety, depression
- Struggle with distorted self, heavy reliance on external validation
- Endless validation-seeking cycle reinforces inadequacy, low self-esteem
- Worsens existing mental health issues, enables harmful behaviors
- Codependent relationships enable substance abuse, self-destructive patterns
- Lack of boundaries leads to loss of individuality, feeling lost and disconnected
- Hinders personal growth, prevents fulfilling, balanced relationships
Read More About Self-Esteem Here
Codependency And Mental Illness
Comorbid mental health conditions can trigger or exacerbate codependency, creating a complex interplay between the two. Here are some mental health disorders 8 Bacon, I., McKay, E., Reynolds, F., & McIntyre, A. (2018). The Lived Experience of Codependency: an Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-018-9983-8 that are commonly associated with codependency:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Substance use disorders
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD)
- Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD)
- Eating disorders
- Bipolar disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Read More About Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Here
How To Recognize The Signs Of Codependency
Recognizing codependency in a clinical setting involves a thorough assessment of an individual’s relationship patterns, emotional responses, and behavioral tendencies. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, are trained to identify 9 O’Brien, P. E., & Gaborit, M. (1992). Codependency: a disorder separate from chemical dependency. Journal of clinical psychology, 48(1), 129–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4679(199201)48:1<129::aid-jclp2270480118>3.0.co;2-c signs of codependency through interviews and observations.
Additionally, the clinician will explore the individual’s past and present relationships to understand how codependent patterns may be impacting their well-being.
While there is no specific clinical diagnostic test for codependency, mental health professionals may use standardized questionnaires and assessments 10 Hughes-Hammer, C., Martsolf, D. S., & Zeller, R. A. (1998). Development and testing of the codependency assessment tool. Archives of psychiatric nursing, 12(5), 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-9417(98)80036-8 to assist in the diagnostic process.
These tools include the “Codependency Assessment Test” by Melody Beattie, the “Codependency Index” developed by Lorna Brown and J. Alan Zimmerman, and the “Codependency Subscale” from the larger Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI). These tests consist of self-report questions related to codependent behaviors and attitudes.
How To Overcome Codependency
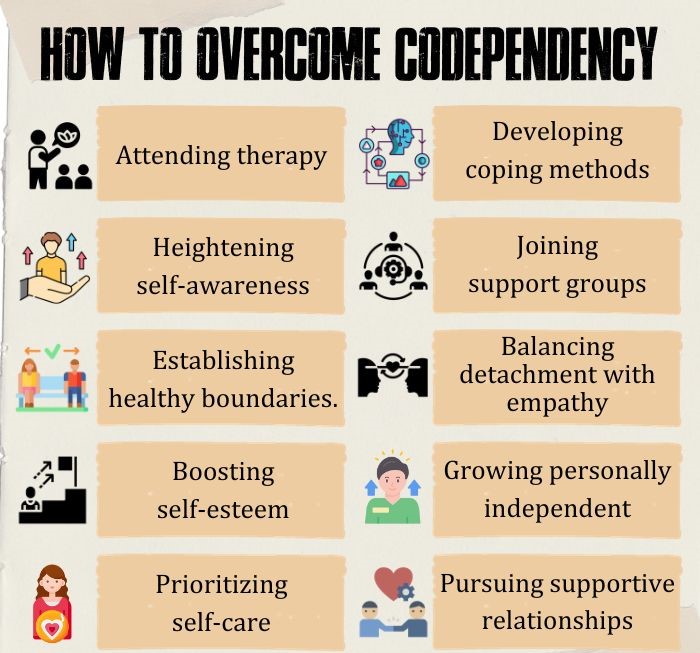
Consider the following measures 11 Panaghi, L., Ahmadabadi, Z., Khosravi, N., Sadeghi, M. S., & Madanipour, A. (2016). Living with Addicted Men and Codependency: The Moderating Effect of Personality Traits. Addiction & health, 8(2), 98–106. on how to overcome codependency:
- Engage in therapy to explore underlying issues and develop healthier relationship patterns.
- Increase self-awareness to identify codependent tendencies and triggers.
- Set and enforce healthy boundaries in relationships to promote self-respect and reduce dependency on others.
- Work on improving self-esteem and self-worth to reduce the need for external validation.
- Prioritize self-care and engage in activities that nurture your well-being and interests.
- Learn healthy ways to cope with emotions and stress without relying solely on others for support.
- Join codependency support groups to connect with others who share similar struggles and learn from their experiences.
- Practice detachment from unhealthy relationships without abandoning empathy and care for others.
- Invest time in personal development and explore interests outside of codependent relationships.
- Seek and nurture relationships that are based on mutual respect, equality, and support.
Read More About Empathy Here
Takeaway
Codependency is a maladaptive dynamic that often arises from underlying issues such as low self-esteem, fear of rejection, and a lack of healthy boundaries. While not classified as a standalone mental health disorder, codependency can significantly impact an individual’s mental health and relationships, making it essential to address and seek professional support to foster healthier patterns of relating and enhance overall well-being.
At A Glance
- Codependency, observed in social relationships, involves one person becoming excessively reliant on another for emotional well-being and self-identity.
- It refers to a dysfunctional pattern where one person relies heavily on another for self-worth and emotional validation.
- Codependent individuals struggle with low self-esteem, lack of boundaries, and an intense need for external approval.
- This can lead to a cycle of enabling and dependency, affecting mental health negatively.
- Though not classified as a mental health disorder, codependency can significantly impact individuals’ emotional wellbeing.
- Codependency and mental illness can fuel each other in the long run.
- Measure on how to overcome codependency include professional support and therapy to foster healthier social bonds.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Are Specific Personality Traits That Make Someone Prone To Codependency?
Specific personality traits that make someone prone to codependency include low self-esteem, people-pleasing tendencies, a strong fear of rejection or abandonment, and a heightened need for external validation.
2. Can Codependency Be Considered A Mental Disorder?
Codependency is not considered a formal mental health disorder but rather a behavioral pattern often associated with other mental health conditions.
3. What Are Some Effective Therapeutic Approaches For Treating Codependency?
Effective therapeutic approaches for treating codependency include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), psychodynamic therapy, and group therapy/support groups focused on codependency.