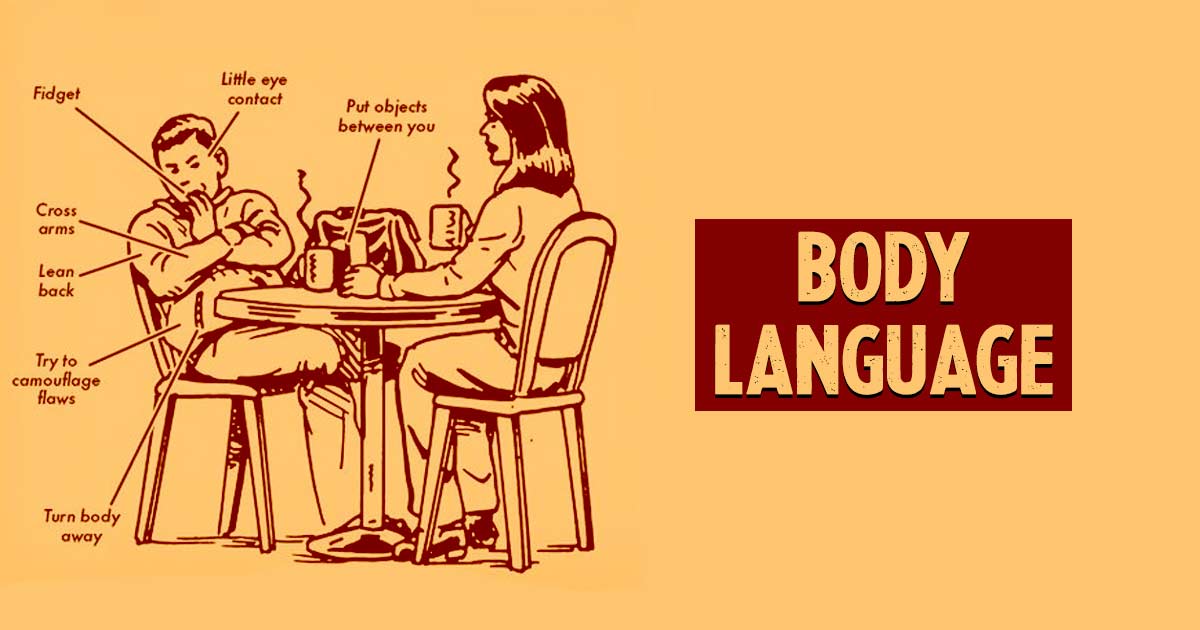
Cluster B personality disorders can be identified by the difficulties regulating one’s emotions and maintaining healthy relationships with others. It involves antisocial personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, histrionic personality disorder & narcissistic personality disorder.
What Are Cluster B Personality Disorders?
Certain environmental factors, early life experiences, and inherited characters influence people’s personalities. Personality is something that makes people different from each other. When a mental health condition affects one’s behavior, thoughts, feelings, personal and professional relationships, it is termed a personality disorder. Mental health professionals diagnose any mental disorder by using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5).
It classifies human personality disorders into three main clusters: cluster A, cluster B, and cluster C. A 2018 research paper 1 Ekselius L. (2018). Personality disorder: a disease in disguise. Upsala journal of medical sciences, 123(4), 194–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009734.2018.1526235 suggested that cluster B is a manifestation of extreme personality disorders that interfere with one’s personal life and cause significant distress, suffering, and functional limitations. This disorder is mostly long-lasting and displays long-term behavioral and inner experiences.
Cluster B personality disorders are related to someone experiencing difficulty in regulating his/her emotions and struggling a lot to maintain healthy relationships. People with these disorders are often extremely dramatic, overly emotional, erratic, and unpredictable in social situations. According to a study 2 Oltmanns, T. F., & Balsis, S. (2011). Personality disorders in later life: questions about the measurement, course, and impact of disorders. Annual review of clinical psychology, 7, 321–349. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-090310-120435 , most people suffer from personality disorders during their adolescence and later life.
Another research paper 3 Fariba K, Gupta V, Kass E. Personality Disorder. [Updated 2021 Feb 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556058/ estimated that 1.5% of the population tends to have the symptoms of these disorders. The symptoms can be long-lasting if not treated properly. This disorder may affect how one thinks about oneself and others, how one reacts emotionally, maintains relationships with others, and controls behavior and feelings.
Traits Of Cluster B personality Disorders

Every personality disorder includes certain unique traits by which one can identify these disorders. The DSM-5 mentions that each trait of cluster B personality disorders should have an onset in early adulthood or adolescence. The guide explains that the traits must be stable over time and these traits should lead to distress or impairment for the sufferers. Cluster B includes four major personality disorders: Antisocial personality disorder, Borderline personality disorder, Histrionic personality disorder, and Narcissistic personality disorder.
These personality disorders are discussed below:
1. Antisocial Personality Disorder
DSM-5 has described antisocial personality disorder as a pattern of disregard for and violation of the physical and emotional rights of others. The symptoms of this disorder are often referred to as sociopathy. However, the term is not used clinically. The development of antisocial personality disorder is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. A study 4 Fisher KA, Hany M. Antisocial Personality Disorder. [Updated 2020 Dec 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546673/ suggested that the prevalence of experiencing the symptoms of this disorder is about 1-4%. The same study estimated that males are 3-5 times more likely to be diagnosed with this disorder. According to a 2002 research paper 5 Bahlmann, M., Preuss, U. W., & Soyka, M. (2002). Chronological relationship between antisocial personality disorder and alcohol dependence. European addiction research, 8(4), 195–200. https://doi.org/10.1159/000066132 , people with this disorder often get addicted to alcohol and drugs.
Certain features of antisocial personality disorder include:
- Having disregard for other people’s feelings and emotions
- Using deceitfulness and manipulation for personal gain
- Intense aggressive behavior towards others may lead to a physical fight
- Treating others harshly and lack of remorse for any harm caused to others
- Recurring problems with the law
- Impulsive behavior and decision making may lead to relationship changes
- Unnecessary lying and assuming false identities
- Irresponsible behavior may affect personal and professional life
- Repeating antisocial actions like harassment and theft
- Acting indifferent to the outcome of hurtful actions and behaviors
- Unnecessary risk-taking with no regard for the safety
- Having poor and abusive relationships
- Having an extreme lack of empathy for others
- Having frequent suicidal thoughts
Causes of antisocial personality disorder
The exact causes of this disorder are not known yet as it needs more detailed research. But some of the significant causes of developing antisocial personality disorder are:
1. Genetics
A 2016 research paper 6 Rautiainen, M. R., Paunio, T., Repo-Tiihonen, E., Virkkunen, M., Ollila, H. M., Sulkava, S., Jolanki, O., Palotie, A., & Tiihonen, J. (2016). Genome-wide association study of antisocial personality disorder. Translational psychiatry, 6(9), e883. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.155 suggested that genetics plays a huge role in making an individual vulnerable to developing the symptoms. Having A family history of antisocial personality disorder or other mental health disorders may increase the risk of developing the symptoms.
2. Life experiences
A 2011 study 7 Tuvblad, C., & Beaver, K. M. (2013). Genetic and environmental influences on antisocial behavior. Journal of criminal justice, 41(5), 273–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrimjus.2013.07.007 stated that childhood experiences and life situations may often trigger the development as well. Diagnosis of childhood conduct disorder or being neglected and abused during childhood or growing up in a chaotic, unhealthy, and violent family environment may be responsible for increasing the symptoms.
2. Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder is associated with chronic instability in behavior, mood, and self-image that often cause unstable relationships. A research paper 8 National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (UK). Borderline Personality Disorder: Treatment and Management. Leicester (UK): British Psychological Society; 2009. (NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 78.) 2, BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK55415/ mentioned that people with this disorder tend to have self-harm and suicidal thoughts. This disorder affects the way one thinks about others and causes problems functioning in everyday life. A 2007 research paper 9 Chapman J, Jamil RT, Fleisher C. Borderline Personality Disorder. [Updated 2021 May 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430883/ suggested that borderline personality disorder affects around 1.6% of the population. It also stated that females are two times more likely to be diagnosed with the symptoms. The symptoms often occur in early childhood and get worse during young adulthood.
Some important features of borderline personality disorder include:
- Engaging in impulsive and risky behavior such as gambling, unsafe sex, binge eating, spending sprees, drug abuse, reckless driving,
- Feeling an intense fear of abandonment or emptiness
- Maintaining unstable intense relationships
- Displaying unstable and fragile self-image
- Rapidly changing life goals and values
- Losing contact with reality and experiencing periods of stress-related paranoia
- Giving suicidal or self-injury threats in response to separation or rejection
- Experiencing extreme mood swings lasted for a long period of time
- Losing temper frequently or intense anger leading to a physical fight
Causes of borderline personality disorder
Like other mental disorders, the actual reasons for developing this disorder are not fully understood. But borderline personality disorder is often associated with:
1. Genetics
A study mentioned that having a twin or any other family member with this personality disorder may increase the risk of developing the symptoms. Studies have found that borderline personality disorder may be inherited and strongly associated with the genetic predispositions.
2. Abnormalities in the brain
A 2012 research paper 10 Soloff, P., Nutche, J., Goradia, D., & Diwadkar, V. (2008). Structural brain abnormalities in borderline personality disorder: a voxel-based morphometry study. Psychiatry research, 164(3), 223–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.02.003 suggested that some areas in the brain responsible for regulating emotions, aggression, and impulsivity are associated with the development of this disorder. When certain brain chemicals such as serotonin don’t function properly, it can cause abnormalities in the brain that may trigger the symptoms.
3. Histrionic Personality Disorder
Histrionic personality disorder can be identified by one’s attention-seeking behavior, self-centeredness, over-dramatic emotions, and sexually provocative actions. According to a research paper 11 French JH, Shrestha S. Histrionic Personality Disorder. [Updated 2020 Nov 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542325/ , the prevalence of experiencing the symptoms of this disorder be 2-3℅ of the population. The same study reported that females tend to be diagnosed with this disorder more than males. Most of these symptoms occur later in life and interfere with the sufferer’s professional and personal life.
Certain key features of histrionic personality disorder include:
- Being an extreme attention-seeker and reaching every extent to be in the limelight
- Changing emotions and behaviors rapidly
- Displaying sexually provocative and seductive behavior
- Acting overly dramatic, often exaggerating emotions and expressions
- Being overly concerned about physical appearance
- Seeking reapproval or reassurance constantly
- Threatening to commit suicide for getting attention
- Impulsive decision making and can be easily influenced by others
- Being extremely self-centered and excessively sensitive to criticism
- Experiencing difficulties in maintaining healthy relationships
- Having two tolerance level and getting bored very easily
Causes of histrionic personality disorder
Mental health professionals suggest that certain learned and inherited factors influence the development of this disorder. The exact causes are not well-known yet, but histrionic personality disorder is often linked to:
1. Heredity
The tendency of this disorder runs in families. That’s why a genetic susceptibility may be inherited for this disorder. Research 12 Reichborn-Kjennerud T. (2010). The genetic epidemiology of personality disorders. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 12(1), 103–114. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2010.12.1/trkjennerud suggested that having a parent with this disorder often increases the risk of the child being diagnosed with it also.
2. Life experiences
Other environmental factors 13 French JH, Shrestha S. Histrionic Personality Disorder. [Updated 2020 Nov 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542325/ also play a very important role. Having an abusive childhood, lack of positive reinforcement, excessive punishments, lack of attention to the child often triggers the symptoms in the child.
4. Narcissistic Personality Disorder
DSM-5 recognizes narcissistic personality disorder as a pattern of a lack of empathy, a sense of entitlement, and a need for extreme admiration. A research paper 14 Mitra P, Fluyau D. Narcissistic Personality Disorder. [Updated 2021 May 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556001/ suggested that 0.5-5% of the population are likely to experience the symptoms of this disorder. Moreover,males tend to experience this disorder more than females. A 2018 study 15 Kacel, E. L., Ennis, N., & Pereira, D. B. (2017). Narcissistic Personality Disorder in Clinical Health Psychology Practice: Case Studies of Comorbid Psychological Distress and Life-Limiting Illness. Behavioral medicine (Washington, D.C.), 43(3), 156–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964289.2017.1301875 explained that a person with narcissistic personality disorder can cause significant distress to even the close ones as they tend to have vulnerable self-esteem and are very sensitive to criticism.
Some features of narcissistic personality disorder include:
- Acting and behaving superiorly with others
- Exaggerating personal achievements in front of others
- Having envy with others unnecessarily
- Having a sense of entitlement and expecting excessive admiration
- Being preoccupied with fantasies of success, power, and beauty
- Belittling people as inferior
- Taking advantage of others for their personal gain
- Unwilling to understand the feelings and needs of others
- Behaving in an arrogant, boastful, and pretentious way
- Having significant interpersonal problems
- Becoming impatient when not receiving special treatment
- Feeling depressed and moody
- Having secret insecurity, shame, and vulnerability
Read More About Narcissism Here
Causes of narcissistic personality disorder
It is not well-identified till now what causes narcissistic personality disorder. The exact causes of developing this disorder are likely to be complex similar to other mental health disorders. But narcissistic personality disorder is often associated with:
1. Life situations
Mismatches in parent-child relationships 16 Mitra P, Fluyau D. Narcissistic Personality Disorder. [Updated 2021 May 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556001/ often lead to the development of this disorder. Excessive criticism and adoration may cause the child to be diagnosed with this disorder in early adulthood.
2. Genetics
A 2014 study 17 Luo, Y. L., Cai, H., & Song, H. (2014). A behavioral genetic study of intrapersonal and interpersonal dimensions of narcissism. PloS one, 9(4), e93403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093403 stated that having a family member with this disorder increases the likelihood of another member experiencing the symptoms during adulthood. Thus, genetics play a significant role in developing this disorder.
Coping With Cluster B Personality Disorders
Cluster B personality disorder sufferers often experience difficulty in maintaining a healthy relationship with others. People with cluster B personality disorders can adapt some self-care strategies to manage the extreme impacts of the symptoms. Although one can manage the negative impact of the symptoms through therapy and coping strategies, personality disorders are not completely curable.
Regular exercises, a healthy diet, meditation, and mindfulness practices can help to boost their mood and reduce frustration. It is important to seek help at the correct time before the symptoms get deteriorated. Supporting someone with these disorders can be challenging, but it is essential to encourage the sufferer for professional help. There are various resources available online through which one can learn how to support people with cluster B personality disorders.