Body image refers to an individual’s emotional and psychological attitudes toward his/her physical appearance. It encompasses how a person perceives and feels about his/her body, including weight, shape, skin, hair, and other physical features.
What Is Body Image?
Body image (BI) refers to an individual’s perception of his/her body and physical appearance—including size, shape, and overall attractiveness.
It involves both the mental picture one has of one’s own body as well as the emotions and attitudes 1 Burychka, D., Miragall, M., & Baños, R. M. (2021). Towards a Comprehensive Understanding of Body Image: Integrating Positive Body Image, Embodiment and Self-Compassion. Psychologica Belgica, 61(1), 248–261. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb.1057 that are associated with that image. It can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health, self-esteem, and behaviors related to food, exercise, and self-care.
Throughout history, body image ideals have varied widely across cultures and time periods. In ancient civilizations, such as Ancient Greece and Rome, the ideal body type for men was muscular and athletic, while for women, it was curvy and voluptuous.
During the Renaissance, fuller figures were also celebrated in both men and women. However, in the 20th century, Western culture began to prioritize thinness as the ideal body type for women, leading to widespread body dissatisfaction and the development of eating disorders. In recent years, there has been a growing movement towards body positivity and acceptance of diverse body types.
Aspects of body image
The four aspects of body image 2 Body Image. (n.d.). ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311962736_Body_Image are as follows:
1. Perceptual
This refers to how a person sees their own body, such as their size, shape, and appearance. People may have a distorted perception of their body, either seeing themselves as larger or smaller than they really are.
2. Affective
This aspect involves the emotional response a person has towards their body, such as feelings of pride or shame. Body image can greatly impact a person’s self-esteem and overall emotional well-being.
3. Cognitive
This refers to the thoughts and beliefs a person has about their body, such as whether they believe it is attractive or unattractive. These thoughts can be influenced by societal standards and cultural norms.
4. Behavioral
This aspect relates to the actions a person takes in response to their body image, such as engaging in exercise or dieting to achieve a certain body type. These behaviors can be healthy or unhealthy, depending on the motivation behind them and the methods used.
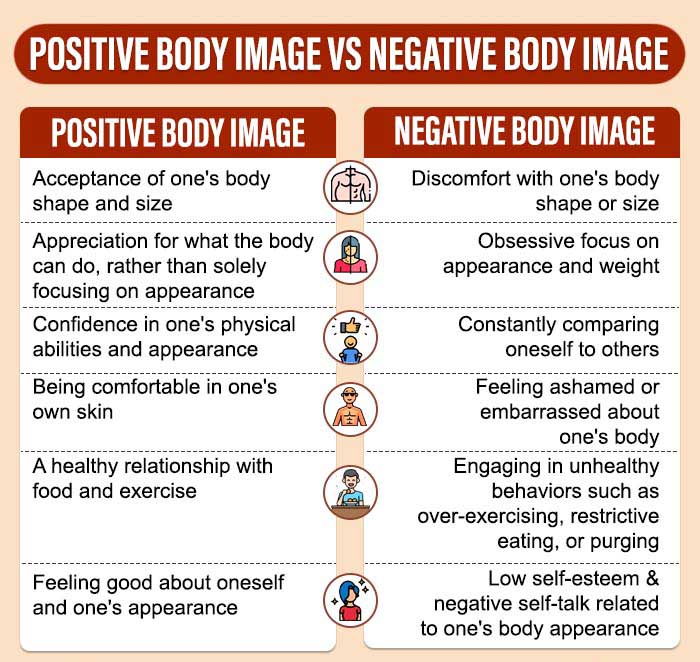
Positive body image vs Negative body image
Body image can be positive or negative. Positive body image refers to 3 Tort-Nasarre, G., Pollina-Pocallet, M., Ferrer Suquet, Y., Ortega Bravo, M., Vilafranca Cartagena, M., & Artigues-Barberà, E. (2023). Positive body image: a qualitative study on the successful experiences of adolescents, teachers and parents. International journal of qualitative studies on health and well-being, 18(1), 2170007. https://doi.org/10.1080/17482631.2023.2170007 having a healthy and realistic perception of one’s body. It involves feeling comfortable and confident in one’s own skin, regardless of societal norms or pressures.
For many people, concerns and anxieties about their bodies can affect their self-esteem and overall well-being, leading to negative body image and mental health issues.
What Are Body Image Issues?
Body image issues refer to a range of negative thoughts, feelings, and attitudes 4 Quittkat, H. L., Hartmann, A. S., Düsing, R., Buhlmann, U., & Vocks, S. (2019). Body Dissatisfaction, Importance of Appearance, and Body Appreciation in Men and Women Over the Lifespan. Frontiers in psychiatry, 10, 864. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00864 toward one’s own physical appearance. These usually result in a preoccupation with one’s appearance and a persistent negative self-image, which can affect an individual’s mental health, self-esteem, and overall well-being. Body image issues usually manifest as:
- Body image distortion 5 Hosseini, S. A., & Padhy, R. K. (2019, September 9). Body image distortion. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546582/
- Dissatisfaction with one’s weight, shape, or size
- Feelings of shame or guilt about one’s body
- Negative self-talk about one’s body
- Self-criticism of one’s body
- Excessive dieting
- Disordered eating (like binge-eating and vomiting)
- Obsession over fitness and exercising
- Getting cosmetic procedures done frequently
Prevalence of body image issues
Negative body image is mostly prevalent in the global population. Studies 6 Kapoor, A., Upadhyay, M. K., & Saini, N. K. (2022). Prevalence, patterns, and determinants of body image dissatisfaction among female undergraduate students of University of Delhi. Journal of family medicine and primary care, 11(5), 2002–2007. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1851_21 show that nearly 70% of women and 50% of men are dissatisfied with their body image. Such body image issues are also closely related to the prevalence of body-related mental health disorders like eating disorders or body dysmorphia.
Reasons For Developing Body Image Issues
The development of negative body image and body dissatisfaction can be influenced by a variety of factors 7 Tort-Nasarre, G., Pollina Pocallet, M., & Artigues-Barberà, E. (2021). The Meaning and Factors That Influence the Concept of Body Image: Systematic Review and Meta-Ethnography from the Perspectives of Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(3), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031140 , including:
- Societal beauty standards that promote an unrealistic definition of beauty
- Pressure to conform to gender, racial, or cultural expectations around appearance
- Media representations of idealized and unattainable body types and over-edited or airbrushed images
- Negative childhood experiences such as bullying, teasing, or constant criticism about appearance
- Traumatic life events, such as sexual assault
- Family history of body image issues and eating disorders
- Physical health conditions related to obesity or malnutrition
- Underlying mental health conditions 8 Satghare, P., Mahesh, M. V., Abdin, E., Chong, S. A., & Subramaniam, M. (2019). The Relative Associations of Body Image Dissatisfaction among Psychiatric Out-Patients in Singapore. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(24), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245162 like depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), PTSD, anxiety, etc.
- Genetics and biological dispositions
- Personal beliefs or values that prioritize appearance over aspects of identity or worth
Read More About Bullying Here
How does social media affect body image?
Social media (especially social media filters and editing tools 9 Aparicio-Martinez, P., Perea-Moreno, A. J., Martinez-Jimenez, M. P., Redel-Macías, M. D., Pagliari, C., & Vaquero-Abellan, M. (2019). Social Media, Thin-Ideal, Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Attitudes: An Exploratory Analysis. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(21), 4177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214177 ) can have a significant impact on body image, as it often promotes unrealistic beauty standards and idealized body shapes.
Seeing constant images of “perfect” bodies can make people feel inadequate about their own bodies, leading to low self-esteem and negative body image. Additionally, social media can foster a culture of comparison and competition, leading to individuals feeling pressure to conform to certain beauty standards.
Negative Body Image And Mental Health
Negative body image can have a significant impact 10 Rodgers, R. F., Laveway, K., Campos, P., & de Carvalho, P. H. B. (2023). Body image as a global mental health concern. Global mental health (Cambridge, England), 10, e9. https://doi.org/10.1017/gmh.2023.2 on an individual’s mental health, self-esteem, and overall well-being. Having a problematic body image based on unrealistic or unachievable beauty standards can result in becoming vulnerable to societal beauty standards and the pressure to conform to appearance-based norms.
Issues of body image can affect a person’s health, driving him/her to display an extreme preoccupation with one’s body shape and size, weight, and perception. He/she also develops a problematic approach to food, particularly developing restrictive eating or unhealthy patterns of food consumption (like self-induced vomiting or binge eating).
It can contribute to poor academic performance, social isolation, and reduced quality of life. In severe cases, the affected person develops a wide range of mental health disorders 11 Verplanken, B., & Velsvik, R. (2008). Habitual negative body image thinking as psychological risk factor in adolescents. Body image, 5(2), 133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2007.11.001 , such as:
- Body dysmorphia
- Eating disorders (like anorexia, bulimia nervosa, etc.) [Read more]
- Depression [Read more]
- Anxiety, particularly social anxiety [Read more]
- Substance use disorder (SUD)
- Self-harm, etc. [Read more]
Treating Negative Body Image Issues
Treatment for body image issues typically involves a combination of approaches 12 Alleva, J. M., Sheeran, P., Webb, T. L., Martijn, C., & Miles, E. (2015). A Meta-Analytic Review of Stand-Alone Interventions to Improve Body Image. PloS one, 10(9), e0139177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139177 , including psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. These include:
1. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
CBT is a type of talk therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thoughts and behaviors. It’s often used to treat body dysmorphic disorder and other related conditions like depression and social anxiety.
Read More About CBT Here
2. Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT)
ACT is a form of therapy that focuses on acceptance, mindfulness, and values-based action. It can help individuals develop a more positive relationship with their bodies and reduce symptoms of negative body image.
3. Group therapy
Group therapy can provide a supportive and encouraging environment for individuals struggling with negative body image. Group therapy can also provide an opportunity to learn from others’ experiences and perspectives.
Read More About Group Therapy Here
4. Nutritional counseling
Nutritional counseling can help individuals develop healthy eating habits and overcome problematic approaches to food. A registered dietitian can provide personalized nutrition counseling based on an individual’s unique needs and preferences.
5. Pharmacotherapy
Antidepressant medications 13 Ipser, J. C., Sander, C., & Stein, D. J. (2009). Pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy for body dysmorphic disorder. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 2009(1), CD005332. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005332.pub2 can be effective in treating conditions such as depression and anxiety, which can be associated with negative body image. However, medication is typically used in conjunction with therapy and healthier lifestyle changes.
How To Overcome Body Image Issues
Overcoming body image issues can be a difficult process, but there are some steps 14 Khalaf, A., Al Hashmi, I., & Al Omari, O. (2021). The Relationship between Body Appreciation and Self-Esteem and Associated Factors among Omani University Students: An Online Cross-Sectional Survey. Journal of obesity, 2021, 5523184. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5523184 you can take to start feeling more comfortable and confident in your own body:
- Try to identify and challenge negative thoughts about your body by asking yourself if they are realistic or fair.
- Practice self-care through regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and mindfulness techniques.
- Spend time with people who are supportive and encouraging about your body perceptions,
- Seek out content media that promotes body positivity and diversity.
- Engage in activities (like a hobby or an interest) that make you feel good, happy, and accomplished.
- If you are struggling with body image issues that are affecting your daily life, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor.
Combating Negative Body Image With Body Positivity
The body positivity movement gained traction as a response to the harmful health effects of societal beauty standards and negative body image.
Body positivity 15 McCallum, M., Ho, A. S., May, C. N., Behr, H., Mitchell, E. S., & Michealides, A. (2021). Body Positivity and Self-Compassion on a Publicly Available Behavior Change Weight Management Program. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(24), 13358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413358 involves promoting self-love and unconditional acceptance of one’s body, regardless of its size or shape. It aims to challenge societal beauty standards, promotes inclusivity and diversity, and does away with a negative and critical attitude toward one’s own physical appearance.
While the body positivity approach has its benefits, it is hardly a balanced road to healthy body image. Studies 16 Simon, K., & Hurst, M. (2021). Body Positivity, but not for everyone: The role of model size in exposure effects on women’s mood, body satisfaction, and food choice. Body image, 39, 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.07.001 reveal that the body-positive approach encourages self-love and indulgences at the cost of healthy lifestyles, often asking people to turn a blind eye to obesity and other sedentary practices.
Some critics argue that body positivity can also perpetuate a focus on physical appearance, as it still centers on the idea of loving or accepting one’s body based on its outward appearance.
Additionally, body positivity can sometimes lead to comparisons, feelings of exclusion, and heightened body surveillance among individuals who do not fit within the traditional beauty ideals celebrated by the movement.
These may include those who do not conform to conventional standards of “big/plus” size, shape, or ability—leading to “thin or skinny shaming”, “muscle shaming”, and so forth.
Body Neutrality: The Quest For A Balanced Body Image
Body neutrality 17 Perry, M., Watson, L., Hayden, L., & Inwards-Breland, D. (2019). Using body neutrality to inform eating disorder management in a gender diverse world. The Lancet. Child & adolescent health, 3(9), 597–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30237-8 is gaining attention as an alternative approach to body positivity—focusing on cultivating a healthy body image with sound mental well-being. It is a concept that aims to promote a neutral and balanced perspective toward one’s own body, rather than a positive or negative one.
It involves accepting and appreciating the functionality of the body, without placing too much emphasis on its appearance. This shifts the focus away from appearance-based goals—such as weight loss or cosmetic procedures—towards health and well-being goals that prioritize overall physical and mental health.

Takeaway
Unresolved issues related to body image can affect a person’s health, mental wellness, daily functioning, and social relationships.
Therefore, understanding what qualifies for a healthy and positive body image, seeking help for body image issues, and finding an approach that works best for oneself comprise the key to enjoying fulfilling body acceptance and satisfaction.
Developing a healthy body image also involves appreciating your body’s abilities, avoiding comparisons, and practicing self-compassion.
It is also crucial to remember that effectively addressing negative body image takes time and patience, so it’s important to focus on progress and small positive changes toward a healthier relationship with your body.
At A Glance
- Body image refers to how an individual perceives and feels about one’s physical appearance, including weight, shape, skin, hair, and other features.
- Negative body image and mental health issues are related due to societal beauty standards, media, childhood experiences, trauma, genetics, and personal beliefs.
- Social media and its filters and editing tools can worsen negative body image.
- Treatment includes psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle changes, group therapy, and nutritional counseling.
- To overcome negative body image, it is important to focus on healthy habits, self-care, and positive self-talk.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who is most affected by body image issues?
People with low self-esteem and poor self-worth are most affected by body image issues.
2. Which celebrities have struggled with body image issues?
In recent years, celebrities like singer Taylor Swift, actress Selena Gomez, singer Demi Lovato, model Bella Hadid, and sportsperson Serena Williams have openly talked about their struggles with body image issues.
3. How does gender affect body image?
Both men and women are equally affected by body image issues. However, the shame around body negativity tends to keep men from seeking treatment or from getting treatment sooner than women.
4. Which age group is most affected by negative body image?
Women and adolescents are more likely to be affected by negative body image.