Arachnophobia is a form of a specific phobia that involves the fear of arachnids such as spiders and scorpions. While most people are usually not very fond of insects, a specific phobia of spiders can affect one’s functioning to a significant degree.
What Is Arachnophobia?
Arachnophobia comes from the Greek word for spider, which is “arachne,” and the Greek word for fear, “phobos”.
Also known as spider phobia, arachnophobia is defined as an acute, abnormal and persistent fear of spiders. Individuals with this phobia experience extreme anxiety, even though they may apprehend that the danger of facing a spider and getting harmed is minimal or nonexistent. The fear can be triggered even on witnessing images of spiders or simply at the mention of them.
A person with this condition may avoid walking barefoot and happen to be alert, especially while taking showers or while getting in and out of bed. Sometimes, the sufferer might take extreme steps to avoid spiders.
Studies 1 Lindner, P., Miloff, A., Reuterskiöld, L., Andersson, G., & Carlbring, P. (2019). What is so frightening about spiders? Self-rated and self-disclosed impact of different characteristics and associations with phobia symptoms. Scandinavian journal of psychology, 60(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12508 show that the fear response is associated more with the movement patterns of the arachnids than their physical appearance. Just like any other phobia, the fear of spiders can weaken you mentally and physically while also interfering with your daily functioning.
It can also lead to an increased fear of other animals that are generally feared or evoke disgust 2 Davey, G. C. L. (1991). Characteristics of individuals with fear of spiders. Anxiety Research, 4(4), 299–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/08917779208248798 . However, once it has been identified, one can get help from experts and eventually go on to live a normal life.
Case Example
When she was around 6 years old, Risha listened to a story by her grandmother in which a man got bitten by a spider and subsequently died.
A few months later, when she was taken to a zoo, she started experiencing nausea as soon as they told her that there was a section nearby where they kept spiders. Before she even saw one with her eyes, Risha fainted. Since then, she had been absolutely terrified of spiders.
She couldn’t even look at pictures or emoticons of spiders without feeling dizzy and experiencing increased breathing and heartbeat rates. Anything that even resembled them would make her extremely uneasy.
Her fear made her wary of public washrooms, nooks and corners, and spaces where there might be spiders. She would mostly avoid outdoor activities and going on trips out of the station due to the possibility of encountering a spider.
Case Analysis
It is clear from Risha’s symptoms that she was experiencing extreme discomfort and suffering from nausea, an increase in heartbeat, fast breathing, dizziness, and loss of consciousness in the actual or imagined presence of spiders. These symptoms suggest that Risha had a specific phobia of spiders or arachnophobia.
How Common Is Arachnophobia?
While specific phobias are quite common, arachnophobia in particular affects around 3.5 to 6.1 per cent of the global population 3 Schmitt, WJ; Müri, RM (2009). “Neurobiologie der Spinnenphobie”. Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie. 160 (8): 352–355 Available from: https://web.archive.org/web/20160823014205/http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=22276624 . Research 4 Hinze, J., Röder, A., Menzie, N., Müller, U., Domschke, K., Riemenschneider, M., & Noll-Hussong, M. (2021). Spider Phobia: Neural Networks Informing Diagnosis and (Virtual/Augmented Reality-Based) Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy-A Narrative Review. Frontiers in psychiatry, 12, 704174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.704174 indicates that women are more prone to develop spider phobia than men.
Read More About Phobia Here
What Is The Psychology Behind Arachnophobia?
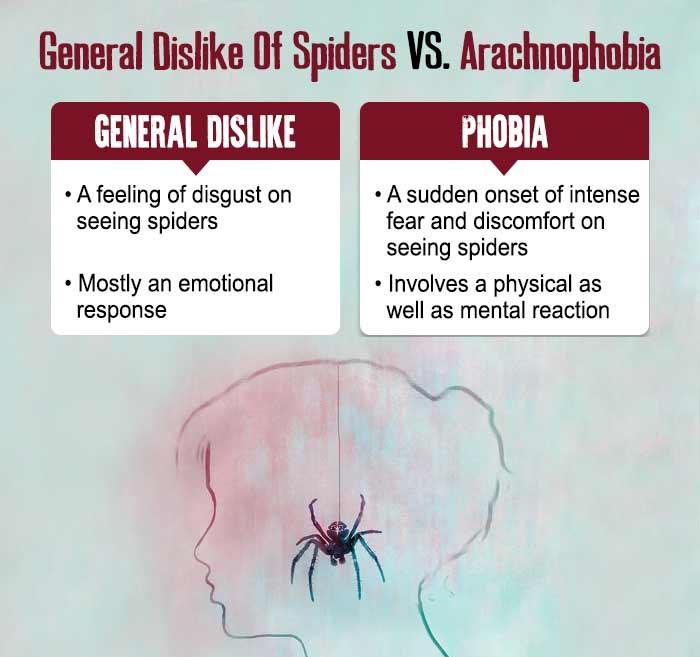
If you are afraid of spiders, that does not necessarily mean you are suffering from arachnophobia. Phobias are a condition of extreme fear that causes a form of paralysis and impairment in a person’s quality of life.
The following are traits of a specific phobia, as per the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5):
1. Extreme & Persistent Fear
If you hold a normal dislike or fear towards a spider, you are most likely to give an expression of disgust or climb onto some furniture while yelling for help.
However, if you are suffering from spider phobia, you will feel extreme anxiety or enter a state of panic, both with the presence and the anticipation or potential presence of spiders.
2. Immediate Fear Response
If you have arachnophobia, the thought of a spider in the near vicinity is just as terrifying as a spider in your hair. When you see a spider or even assume that you might see one, your anxiety and panic are likely to be immediate.
However, in some arachnophobes, the presence or the assumed presence of a spider does not always provoke a panic attack. Such individuals are more likely to experience severe fear if they feel trapped with the spider in the same room or house.
3. Avoidance
A person with arachnophobia will avoid a spider at any cost. You might end up cleaning your house for hours or sleeping at your friend’s place if you see a spider in your house.
You’ll also avoid the outdoors or the basement of your house as you fear that you may run into one. Such actions may interfere with various aspects of your life, like your relationship, work, and how you spend your time.
Symptoms Of Arachnophobia
Here are the most common physical and behavioral symptoms 5 NHS. (2021, February 15). Symptoms – Phobias. Nhs.uk. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/phobias/symptoms/ of this condition –
1. Physical Symptoms
The most observed physical symptoms associated with this phobia are:
- Feeling a sense of dizziness or lightheadedness
- Suffering from an upset stomach
- Feeling nausea
- Sweating profusely while shaking or trembling with fear
- Experiencing shortness of breath
- Increased heart rate
- Fainting out of fear
2. Behavioral Symptoms
Apart from the physical symptoms, a person with arachnophobia may also display behavioral symptoms such as:
- Unexplainable alertness connected to the spiders along with the obsession of checking the presence of spiders before going anywhere.
- Avoiding places where spiders can be usually found such as caves, forests, museums, or old buildings.
- Avoiding activities such as hiking and camping trips. Avoiding places connected to a negative past experience with spiders. Difficulty with concentration and functioning at work or in personal relationships
- Avoiding social gatherings.

What Causes Arachnophobia?
Although the exact causes of onset are still unclear, here are some possible factors that can lead to the development of such specific phobia –
1. Evolutionary Theory
According to evolutionary theory 6 Hendry, A. P., Kinnison, M. T., Heino, M., Day, T., Smith, T. B., Fitt, G., Bergstrom, C. T., Oakeshott, J., Jørgensen, P. S., Zalucki, M. P., Gilchrist, G., Southerton, S., Sih, A., Strauss, S., Denison, R. F., & Carroll, S. P. (2011). Evolutionary principles and their practical application. Evolutionary applications, 4(2), 159–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-4571.2010.00165.x , this phobia is a result of a survival method for our ancestors. Since most spiders are poisonous or deadly, a fear of spiders may have made humans more likely to survive and reproduce.
2. Social Theories
Another theory suggests that the fear of spiders in humans is learned. For example, the media or TV shows often describe spiders as scary and potentially dangerous.
Additionally, as a child, if you grow up in an environment where the elders or your parents are scared of spiders, this may lead to learned behavior 7 Shechner, T., Hong, M., Britton, J. C., Pine, D. S., & Fox, N. A. (2014). Fear conditioning and extinction across development: evidence from human studies and animal models. Biological psychology, 100, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.04.001 , thereby leading you to develop the same fear.
3. Traumatic Past Experience
Phobias often originate or arise from negative past experiences. Hence, it is likely for one’s fear of spiders to develop as a result of certain negative experiences with such arthropods. . With time, this fear of spiders may develop into arachnophobia.
4. Cultural Background
Some experts also theorize that the fear of spiders is inspired by one’s cultural background. For example, in certain regions of Africa, large spiders are feared. However, in South Africa, where spiders are eaten, people may feel unafraid of them.
Arachnophobia Diagnosis
Arachnophobia does not usually require a formal diagnosis from a doctor as phobias are more or less often self-diagnosable. However, it is a wiser decision to seek professional help to enable you to work through your spider phobia.
Consider asking yourself a few questions that may help you to understand whether the fear is interfering with your day-to-day activities.
- Is the fear of spiders making it difficult for you to go outdoors?
- Is it getting in the way of your work?
- Is it affecting your social life?
- Is it stopping you from spending time with your loved ones?
- Does the fear of spiders keep you awake at night?
- Are you not able to stop thinking about spiders?
If the answer to these questions is ”yes”, you may consider seeing a psychotherapist. However, to diagnose the condition as arachnophobia, the symptoms should be occurring for more than six months and it should be intense enough to disrupt your daily life activities and needs.
How To Treat Fear Of Spiders
Specific phobias such as arachnophobia are relatively easier to treat when compared to complex phobias. Chances are high that with age, symptoms of arachnophobia may decrease. The arachnophobia treatment may be in the form of therapy or medication, depending on the severity of your symptoms and preferences.
Here are the most common and effective treatment approaches for this condition –
1. Therapy
Studies 8 De Jong, P. J., Andrea, H., & Muris, P. (1997). Spider phobia in children: disgust and fear before and after treatment. Behaviour research and therapy, 35(6), 559–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-7967(97)00002-8 have found that behavioral therapy-based treatment can prove effective for treating spider phobia, especially in children. Here are some therapy approaches widely recommended by healthcare professionals –
A. Exposure therapy
Exposure therapy is a process wherein the patient is directly exposed to their phobia, in this case, a spider. A study 9 Hoffman, Y. S. G., Pitcho-Prelorentzos, S., Ring, L., & Ben-Ezra, M. (2019). “Spidey Can”: Preliminary Evidence Showing Arachnophobia Symptom Reduction Due to Superhero Movie Exposure. Frontiers in psychiatry, 10, 354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00354 said that making the person watch arachnid or insect-themed superhero movies, like “Spider-Man or Ant-Man” can help reduce phobic symptoms.
A type of exposure therapy is called flooding. Here, the person is exposed to their phobia in full intensity by the therapist in an attempt to decrease their anxiety.
B. Hypnotherapy
Hypnosis can also help a person overcome arachnophobia. Hypnotherapy 10 Hirsch J. A. (2018). Integrating Hypnosis with Other Therapies for Treating Specific Phobias: A Case Series. The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 60(4), 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/00029157.2017.1326372 uses relaxation techniques to provoke a state of focused attention. The therapist will then use techniques and guided representation to help reduce phobia. However, there is a lack of scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of this treatment.
C. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
In cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), the therapist works with the patient to help them overcome their fearful thoughts. CBT techniques are considered to be one of the most effective treatments for specific phobias, as validated by a recent 2021 study 11 Hinze, J., Röder, A., Menzie, N., Müller, U., Domschke, K., Riemenschneider, M., & Noll-Hussong, M. (2021). Spider Phobia: Neural Networks Informing Diagnosis and (Virtual/Augmented Reality-Based) Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy-A Narrative Review. Frontiers in psychiatry, 12, 704174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.704174 .
Read More About CBT Here
2. Medication
Medications for arachnophobia are mostly directed at symptom management and cannot treat the root of the disorder. However, they may help to improve the anxiety symptoms to a large extent. Options for medications include:
- Antidepressants
- Beta-Blockers
- Sedatives
- Supplements for anxiety
- Tranquilizers, etc.
For better results, a combination of therapy sessions and medication may be used to treat arachnophobia. Relaxation techniques such as meditation can also be effective in the treatment of arachnophobia.
Ways To Cope With Arachnophobia
Here are some self-help coping strategies that can help you overcome your fear of spiders –
1. Learn more about spiders
Spider phobia can also develop owing to some misconceptions about spiders.. Hence, to help yourself to overcome this phobia, you can try to read up on some non-threatening facts about spiders.
One of the first things that you might learn is that spiders rarely bite until and unless they feel threatened and rarely do spider bites cause an allergic reaction. Very few spider bites are venomous or dangerous. In fact, most of the bites are actually harmless.
Also, it must be noted that spiders in general (including the much-feared black widow and brown recluse) bite only when they feel trapped between your skin and another object.
Also, there are more than 63,000 species of spiders in the world and only 2% of them are dangerous. Moreover, your chance of coming in contact with that 2% is even lesser.
2. Build a Healthy Environment
Make sure to store firewood outside your house to avoid bringing spiders into the house. Place well-fitted screens on your doors and windows to stop the entrance of spiders in your house along with sealing any cracks wherever possible.
Avoid keeping rocks or lumber right outside your house as spiders are found in such areas and keep your attic and garage free of spider webs.
3. Talk it Out to Feel Less Stressed
Discuss your fear with your close ones and inform them about your treatment. Ask your healthcare provider to prescribe a professional who can assist you overcome your arachnophobia.
4. Write Down Your Fear
Figure out your negative beliefs and thought patterns about spiders that make your anxiety worse and write down the same in a journal or a diary. This way you can pick out specific beliefs and repetitive thoughts that are misleading and systematically replace them with positive thoughts.
5. Lifestyle Changes
You can adopt better lifestyle changes such as working out regularly and maintaining a healthy diet to reduce your anxiety along with the symptoms of the phobia.
The key to overcoming such a phobia is commitment and faith. Remember that spiders are not as dangerous or fatal as it is perceived to be and seeking the truth is one of the best ways to overcome arachnophobia.
Takeaway
Arachnophobia is a form of specific phobia that can arise at any time during a person’s life. However, there are ways to cope with arachnophobia and prevent it from interfering with your life. Therapy is the most efficient path to deal with spider phobias.
The sooner you work to fight your phobias, the better you will feel. However, overcoming arachnophobia is not an overnight trick. It is a time taking process which will require complete commitment.
At A Glance
- Arachnophobia is the specific phobia of spiders
- Being a clinical phobia, it is different from the common dislike of spiders.
- Like other phobias, its symptoms involve nausea, breathing problems, fainting, avoiding outdoor activities, etc.
- Its causes are attributed to past negative experiences associated with spiders, cultural influence, learned behavior, etc.
- Most of the time, the excessive fear of spiders decreases with age.
- It is also easily treatable by a number of therapies, medication, and self-help coping techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is Arachnophobia hereditary?
There could be a genetic risk for specific phobias, including arachnophobia. If your family member or relative is afraid of spiders, you can be more likely to develop the phobia. However, it is not the only risk factor, as the environment and other things also play a major role.
2. Can Arachnophobia kill you?
According to the DSM, people with specific phobias do have an increased risk of suicide. However, it is less common than other anxiety disorders.
3. Is Arachnophobia curable?
Yes. Arachnophobia can be cured with the help of regular therapy, and/or medication.