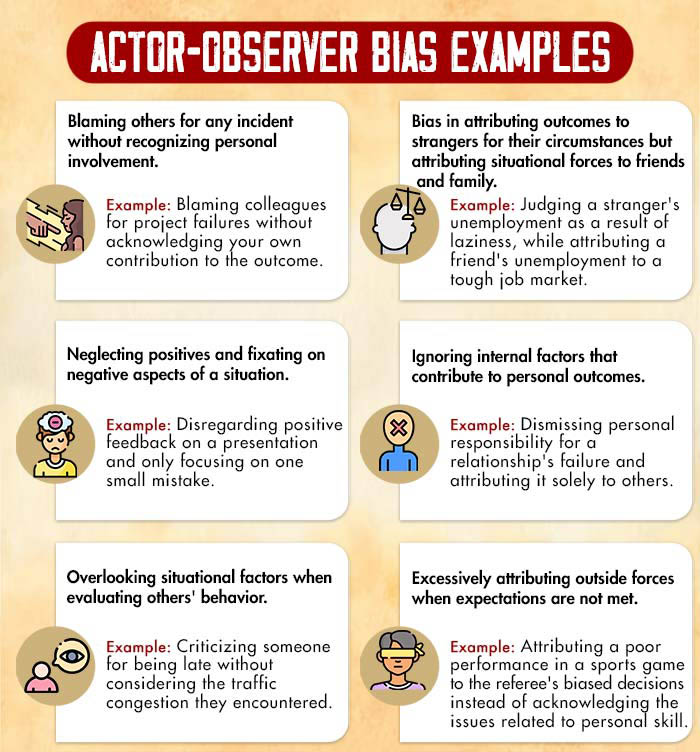
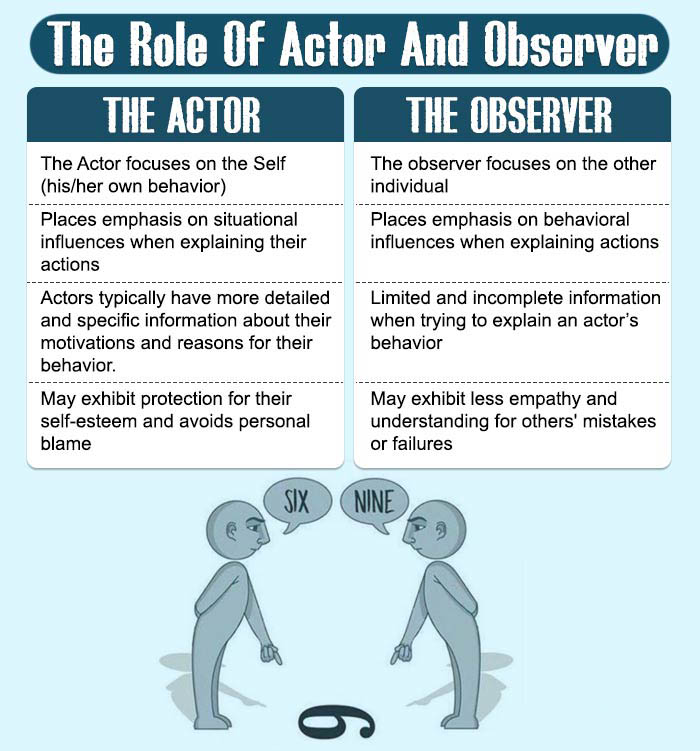
The actor-observer bias refers to individuals attributing their own behavior to situational factors and others’ behavior to personal traits. This bias can result in misunderstandings and conflicts, adversely affecting mental health functioning and overall well-being.
What is Actor-Observer Bias?
The actor-observer bias is a common bias 1 Koenig, A. (2013). Actor‐Observer Bias. 19–20. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118339893.wbeccp008 observed in social interactions and perceptions. When individuals are the “actor” in a situation, they tend to focus on the situational context that influenced their behavior, leading them to attribute their actions to external factors such as circumstances, pressure or other people’s influence.
On the other hand, when individuals are the “observer” and interpret the behavior of others, they tend to attribute their actions to internal characteristics or dispositional factors, such as personality traits or inherent qualities.
For example, when individuals are running late 2 Nadelhoffer, T., & Feltz, A. (2008). The Actor–Observer Bias and Moral Intuitions: Adding Fuel to Sinnott-Armstrong’s Fire. Neuroethics, 1(2), 133–144. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12152-008-9015-7 , they tend to attribute their behavior to external factors, such as traffic congestion or unexpected circumstances, as the actor. However, as observers, they often attribute others’ behavior to personal traits like laziness or lack of responsibility. Research indicates that women are 3 Marsh, R. L., Cook, G. I., & Hicks, J. L. (2006). Gender and orientation stereotypes bias source-monitoring attributions. Memory (Hove, England), 14(2), 148–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658210544000015 more likely than men to use these external attributions.
Causes of the Actor-Observer Bias
Some causes of 4 The Influence of Actor Observer Bias on Attributions of Other Drivers. (n.d.). ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240136177_The_Influence_of_Actor_Observer_Bias_on_Attributions_of_Other_Drivers the actor-observer bias include:
1. Perceptual Differences
In everyday situations, individuals tend to focus more on their thoughts, feelings, and the circumstances surrounding them when considering the reasons behind their actions. However, when it comes to understanding why others behave the way they do, people often pay more attention to what they can directly see and observe about those individuals.
2. Informational Differences
People have more direct access to their thoughts, emotions, and situational factors compared to the limited information available when observing others. This information asymmetry can lead to biased judgments and attributions.
3. Motivational Differences
Motives play a significant role in actor-observer bias, including the need to enhance or protect one’s self-esteem. This bias is particularly evident in negative situations where blame-worthy behavior occurs. To protect their self-esteem, individuals tend to point to external factors, placing the blame on others rather than accepting full responsibility for their own behavior.
Impact of the Actor-Observer Bias on Mental Health
The impact of the actor-observer bias on mental health 5 Robins, R. W., Spranca, M. D., & Mendelsohn, G. A. (1996). The actor-observer effect revisited: effects of individual differences and repeated social interactions on actor and observer attributions. Journal of personality and social psychology, 71(2), 375–389. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.71.2.375 can be significant and includes:
- As individuals attribute their behavior to external factors but attribute the behavior of others to internal traits it can create misunderstandings and interpersonal conflicts.
- By failing to consider external factors influencing others’ actions, individuals may struggle to understand and empathize with their experiences.
- When people consistently attribute their behavior to external factors, they may struggle to take personal responsibility for their actions.
- Misattributing others’ behavior to internal traits can fuel negative judgments, hostility, and passive aggression, causing elevated levels of stress and anxiety in social situations.
- When individuals consistently attribute others’ behavior to internal traits, it can create a lack of social support and loneliness.
Read More About Loneliness Here
How to Avoid the Actor-Observer Bias
To avoid the actor-observer bias, consider the following strategies 6 Malle, B. F., Knobe, J. M., & Nelson, S. E. (2007). Actor-observer asymmetries in explanations of behavior: new answers to an old question. Journal of personality and social psychology, 93(4), 491–514. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.93.4.491 :
- Try to put yourself in their shoes and make an effort to understand the emotions and experiences of others.
- Try to find a solution related to any problem rather than blaming others for it.
- Practice gratitude to foster a positive perspective and reduce bias.
- Learn about the signs of cognitive biases especially the actor-observer bias examples, to become more aware of their influence.
- Actively listen, consider alternative explanations, and avoid jumping to conclusions based solely on dispositional attributions.
- Seek feedback from trusted individuals to gain broader insights and foster personal growth.
- Acknowledge your role in actions and decisions, avoiding excessive external attributions.
- Engage in practices like journaling, mindfulness, or meditation to deepen self-understanding and uncover biases.
Read More About Mindfulness Here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between actor-observer bias vs. fundamental attribution error?
The fundamental attribution error focuses primarily on explaining the behavior and attributes of others, while the actor-observer bias extends its scope to include both the behavior of the individual and the behavior of others.
2. Can awareness of the actor-observer bias improve relationships?
Awareness of the actor-observer bias fosters stronger relationships by deepening understanding and mitigating conflicts that may arise from the tendency to make biased attributions.
3. Are there cultural variations in the prevalence of the actor-observer bias?
Cultural variations can influence the prevalence and manifestation of actor-observer bias, as cultural norms, values, and socialization processes may shape individuals’ attribution tendencies.