- Recent studies raised concerns about the increasing instances of antidepressant addiction.
- Long-term exposure to these psychotropic drugs creates the potential for dependence and withdrawal—akin to substance addiction.
Are Antidepressants Addictive?
The classification of antidepressants as addictive and the topic of antidepressant addiction are subjects of ongoing debate within the medical community.
Generally, antidepressants are not considered addictive in the same way as substances like opioids or stimulants. Unlike addictive drugs, antidepressants do not produce the euphoric “high” or cravings typically associated with addiction.
However, it is important to note that discontinuing antidepressants abruptly can result in withdrawal symptoms—which are distinct in addiction or substance use disorder (SUD). A recent study by researchers at University College London (UK) claims that when an individual exhibits symptoms such as dizziness, insomnia, or irritability upon discontinuing a prolonged course of antidepressants, it suggests the potential for dependence or addiction.
Most people confuse this post-treatment “antidepressant withdrawal” as relapsed depression or other mental health disorders for which the antidepressants are usually prescribed. These may include:
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Anxiety and panic disorder
- Phobias
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Body dysmorphia, etc.
Symptoms Of Antidepressant Addiction
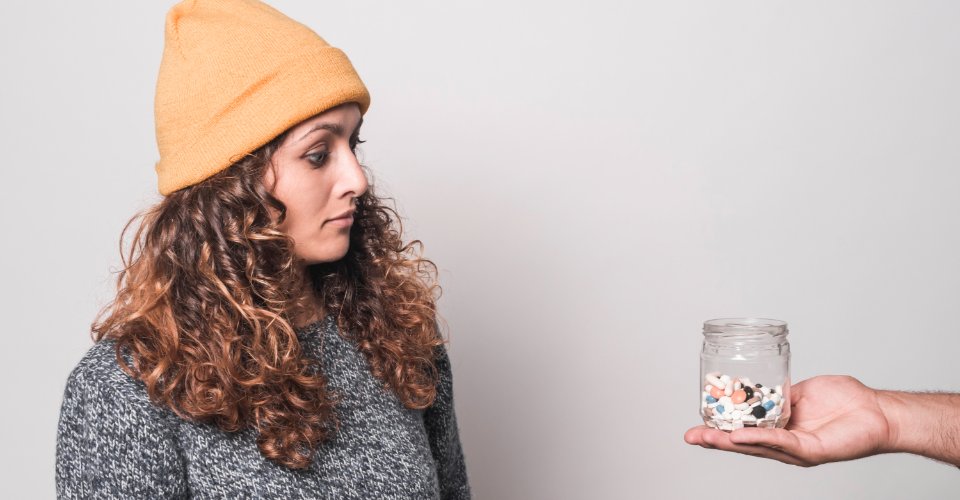
Although antidepressant addiction is rare, some individuals may misuse or abuse these medications. Signs of antidepressant abuse may include:
- Taking higher doses than prescribed
- Using antidepressants recreationally
- Combining antidepressants with other substances
- Seeking multiple prescriptions from different doctors
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms if discontinuing antidepressants
Examples Of Addictive Antidepressants
Examples of antidepressants that may have a risk of dependence or withdrawal symptoms include:
- Venlafaxine (Effexor): Abruptly stopping venlafaxine can lead to discontinuation syndrome, which may involve symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, headache, and mood changes.
- Paroxetine (Paxil): Discontinuing paroxetine suddenly can result in withdrawal symptoms, including flu-like symptoms, sleep disturbances, and mood swings.
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta): Withdrawal symptoms, such as dizziness, nausea, headache, and mood changes, have been reported when stopping duloxetine abruptly.
Addressing Addiction To Antidepressants
Antidepressant addiction cases are not indicative of addiction in the traditional sense, but rather a potential for dependence or withdrawal effects when the medication is stopped abruptly or without medical supervision. If you think that you are edging toward addiction to antidepressants, consider adhering to the following guidelines:
- Take the medication as prescribed, without skipping doses.
- Follow the recommendations provided by the healthcare professional precisely.
- Avoid combining antidepressants with other substances, including alcohol.
- Be aware that long-term administration of antidepressants can lead to dependency.
- If any adverse side effects are noticed, inform the specialist promptly so they can adjust the dosage or prescribe an alternative medication.
- Consider undergoing genetic tests to assess the potential effects of the drugs.
- It is important to note that while antidepressants treat symptoms, addressing the underlying issues requires psychological therapy to facilitate the patient’s ability to discontinue pharmacological treatment.
The misuse of any substance, specifically antidepressants, can potentially lead to addiction and exacerbate mental health symptoms.
Therefore, it is crucial to consult with specialized professionals and follow their instructions. When taken correctly, these medications are safe and effective, and there may come a time in our lives when we may require them.