In our tumultuous journey through life, stress is a constant companion. It’s an unwelcome guest that arrives unannounced, due to the everyday pressures of work, social commitments, and unforeseen challenges. While occasional stress may be a natural part of life, extensive research has illuminated the perilous path that chronic stress can pave toward long-term health consequences.
Beyond its immediate impacts on sleep and mood, stress exerts a subtler, more insidious influence on what and how we eat.
The term “diet” encompasses a multifaceted array of factors, including food choices, appetite, and digestion, all of which can fall prey to the underhanded effects of stress.
In essence, stress might be stealthily sabotaging your health goals in ways you may not even realize. In this report, we delve into the intricate relationship between stress and dietary habits, shedding light on how stress might be affecting your diet and what proactive measures can be taken to prevent it from undermining your health.
Stress is not merely an emotional state but a comprehensive assault on your physical and mental well-being. Chronic stress, in particular, wields a significant impact on the human body, affecting sleep patterns, mood regulation, and, crucially, dietary choices.
The connection between stress and eating habits is far more intricate than one might assume.
Chronic stress’s detrimental effects on the body are well-documented, with its potential to disrupt sleep patterns, plunge moods into darkness, and subtly manipulate eating behaviors.
To comprehend the nuances of this relationship, it’s essential to understand how stress extends its reach beyond the immediate physiological responses.
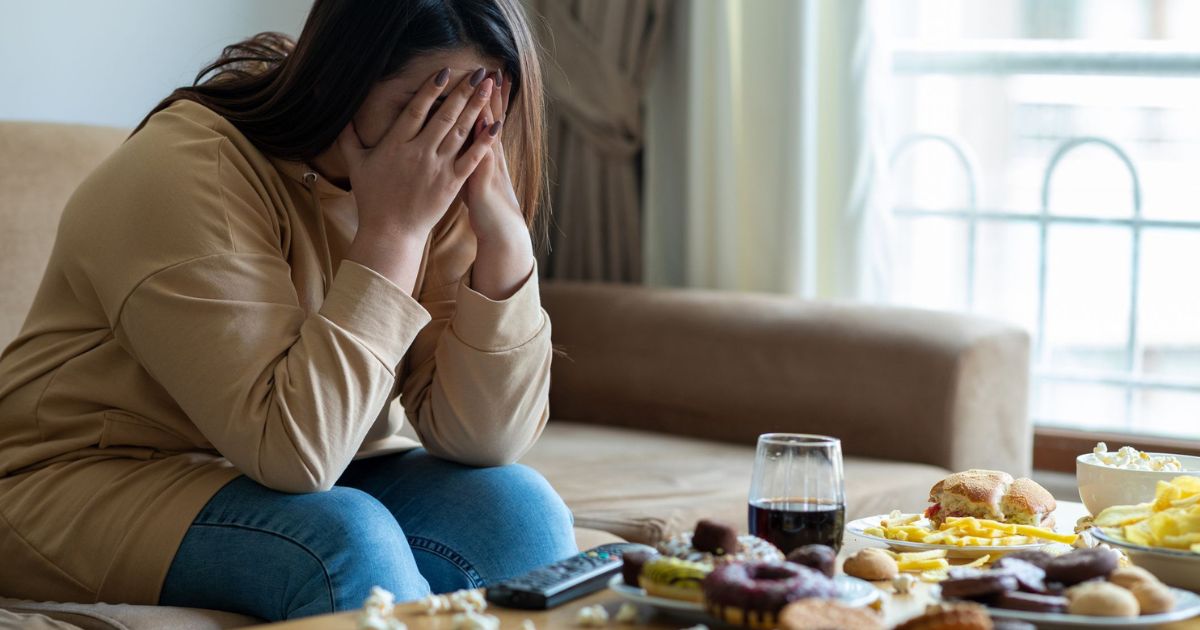
While acute stress can sometimes lead to appetite suppression, chronic stress often has the opposite effect, triggering cravings for high-calorie, comfort foods rich in sugar and fat. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as “stress eating” and occurs as a result of complex interactions between hormones and neurotransmitters in the body.
One of the key players in stress-induced dietary changes is cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone.” Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which, in turn, can increase your appetite and lead to overeating, particularly when it comes to foods that provide a quick energy boost.
Simultaneously, chronic stress can interfere with the body’s natural hunger and fullness cues, making it more challenging to regulate food intake sensibly.
Furthermore, the emotional toll of chronic stress can lead to emotional eating, where food is used as a coping mechanism to soothe negative emotions. Stress often leads to feelings of anxiety, sadness, or frustration, and individuals may turn to food as a source of comfort, irrespective of physical hunger.
The Brain-Bending Effects of Chronic Stress
Beyond the hormonal and physiological factors at play, chronic stress also exerts a profound impact on the brain. It has the potential to reshape habits and decision-making processes, often steering individuals toward less healthy dietary choices.
This cognitive aspect of stress’s influence is rooted in the intricate neural pathways that govern behavior.
Chronic stress can impair the brain’s prefrontal cortex, a region responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, impulse control, and goal-setting.
Consequently, individuals under chronic stress may find it challenging to resist the allure of unhealthy foods and are more likely to succumb to impulsive choices that prioritize immediate gratification over long-term health goals.
Furthermore, stress can lead to a heightened susceptibility to reward-based eating, where individuals seek out foods that provide a pleasurable sensation.
This inclination can lead to a vicious cycle of stress-induced eating, as indulging in such foods provides temporary relief from stress-related emotions.
Mitigating Stress’s Impact on Your Diet
While the relationship between stress and dietary habits may seem daunting, there are proactive measures you can take to regain control and protect your health goals.
- Stress Management: Implement stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, exercise, and deep breathing exercises to mitigate chronic stress’s emotional toll.
- Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating by paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. This can help you distinguish between emotional and physical hunger and make more conscious food choices.
- Healthy Alternatives: Stock your pantry and fridge with nutritious, satisfying alternatives to comfort foods. Having healthier options readily available can reduce the temptation to reach for sugary or fatty snacks during stressful times.
- Seek Support: Consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor if emotional eating becomes a persistent issue. Therapy can provide valuable tools for managing stress and emotions in healthier ways.
- Routine and Self-Care: Establish a daily routine that includes regular meals, adequate sleep, and self-care practices. Consistency can help stabilize your mood and reduce stress-induced disruptions in eating patterns.
In conclusion, the intricate dance between chronic stress and dietary habits highlights the profound impact stress can have on our well-being.
While stress may be an unavoidable part of life, understanding its subtle influences on our diet empowers us to make more informed choices.
By implementing stress management strategies and adopting mindful eating practices, we can regain control over our dietary decisions and prevent stress from silently sabotaging our health goals.